Structural and biochemical characterization of Staphylococcus aureus clumping factor B/ligand interactions
- PMID: 21543319
- PMCID: PMC3138276
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.217414
Structural and biochemical characterization of Staphylococcus aureus clumping factor B/ligand interactions
Abstract
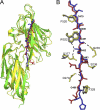
Clumping factor B (ClfB) from Staphylococcus aureus is a bifunctional protein that binds to human cytokeratin 10 (K10) and fibrinogen (Fg). ClfB has been implicated in S. aureus colonization of nasal epithelium and is therefore a key virulence factor. People colonized with S. aureus are at an increased risk for invasive staphylococcal disease. In this study, we have determined the crystal structures of the ligand-binding region of ClfB in an apo-form and in complex with human K10 and Fg α-chain-derived peptides, respectively. We have determined the structures of MSCRAMM binding to two ligands with different sequences in the same site showing the versatile nature of the ligand recognition mode of microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules. Both ligands bind ClfB by parallel β-sheet complementation as observed for the clumping factor A·γ-chain peptide complex. The β-sheet complementation is shorter in the ClfB·Fg α-chain peptide complex. The structures show that several residues in ClfB are important for binding to both ligands, whereas others only make contact with one of the ligands. A common motif GSSGXG found in both ligands is part of the ClfB-binding site. This motif is found in many human proteins thus raising the possibility that ClfB recognizes additional ligands.
Figures




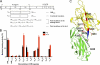
References
-
- Diekema D. J., Pfaller M. A., Schmitz F. J., Smayevsky J., Bell J., Jones R. N., Beach M. (2001) Clin. Infect. Dis. 32, S114–S132 - PubMed
-
- Lowy F. D. (1998) N. Engl. J. Med. 339, 520–532 - PubMed
-
- Chambers H. F. (2009) J. Infect. Dis. 199, 291–293 - PubMed
-
- von Eiff C., Becker K., Machka K., Stammer H., Peters G. (2001) N. Engl. J. Med. 344, 11–16 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

