First structural glimpse of CCN3 and CCN5 multifunctional signaling regulators elucidated by small angle x-ray scattering
- PMID: 21543320
- PMCID: PMC3121370
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.225755
First structural glimpse of CCN3 and CCN5 multifunctional signaling regulators elucidated by small angle x-ray scattering
Abstract
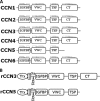
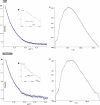
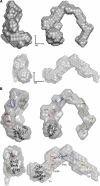
The CCN (cyr61, ctgf, nov) proteins (CCN1-6) are an important family of matricellular regulatory factors involved in internal and external cell signaling. They are central to essential biological processes such as adhesion, proliferation, angiogenesis, tumorigenesis, wound healing, and modulation of the extracellular matrix. They possess a highly conserved modular structure with four distinct modules that interact with a wide range of regulatory proteins and ligands. However, at the structural level, little is known although their biological function(s) seems to require cooperation between individual modules. Here we present for the first time structural determinants of two of the CCN family members, CCN3 and CCN5 (expressed in Escherichia coli), using small angle x-ray scattering. The results provide a description of the overall molecular shape and possible general three-dimensional modular arrangement for CCN proteins. These data unequivocally provide insight of the nature of CCN protein(s) in solution and thus important insight into their structure-function relationships.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

