Regulation of Src family kinases involved in T cell receptor signaling by protein-tyrosine phosphatase CD148
- PMID: 21543337
- PMCID: PMC3121354
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.196733
Regulation of Src family kinases involved in T cell receptor signaling by protein-tyrosine phosphatase CD148
Abstract
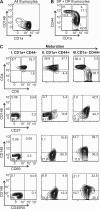
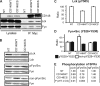
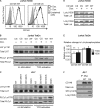
CD148 is a receptor-like protein-tyrosine phosphatase known to inhibit transduction of mitogenic signals in non-hematopoietic cells. Similarly, in the hematopoietic lineage, CD148 inhibited signal transduction downstream of T cell receptor. However, it also augmented immunoreceptor signaling in B cells and macrophages via dephosphorylating C-terminal tyrosine of Src family kinases (SFK). Accordingly, endogenous CD148 compensated for the loss of the main SFK activator CD45 in murine B cells and macrophages but not in T cells. Hypothetical explanations for the difference between T cells and other leukocyte lineages include the inability of CD148 to dephosphorylate a specific set of SFKs involved in T cell activation or the lack of CD148 expression during critical stages of T cell development. Here we describe striking differences in CD148 expression between human and murine thymocyte subsets, the only unifying feature being the absence of CD148 during the positive selection when the major developmental block occurs under CD45 deficiency. Moreover, we demonstrate that similar to CD45, CD148 has both activating and inhibitory effects on the SFKs involved in TCR signaling. However, in the absence of CD45, activating effects prevail, resulting in functional complementation of CD45 deficiency in human T cell lines. Importantly, this is independent of the tyrosines in the CD148 C-terminal tail, contradicting the recently proposed phosphotyrosine displacement model as a mechanism of SFK activation by CD148. Collectively, our data suggest that differential effects of CD148 in T cells and other leukocyte subsets cannot be explained by the CD148 inability to activate T cell SFKs but rather by its dual inhibitory/activatory function and specific expression pattern.
Figures





References
-
- Honda H., Inazawa J., Nishida J., Yazaki Y., Hirai H. (1994) Blood 84, 4186–4194 - PubMed
-
- Kuramochi S., Matsuda S., Matsuda Y., Saitoh T., Ohsugi M., Yamamoto T. (1996) FEBS Lett. 378, 7–14 - PubMed
-
- Zhang L., Martelli M. L., Battaglia C., Trapasso F., Tramontano D., Viglietto G., Porcellini A., Santoro M., Fusco A. (1997) Exp. Cell Res. 235, 62–70 - PubMed
-
- Autschbach F., Palou E., Mechtersheimer G., Rohr C., Pirotto F., Gassler N., Otto H. F., Schraven B., Gaya A. (1999) Tissue Antigens 54, 485–498 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

