Mutational analysis of the necdin gene in patients with congenital isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
- PMID: 21543378
- PMCID: PMC3203643
- DOI: 10.1530/EJE-11-0199
Mutational analysis of the necdin gene in patients with congenital isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Abstract
Context: Necdin activates GNRH gene expression and is fundamental for the development, migration, and axonal extension of murine GNRH neurons. In humans, necdin plays a potential role in the hypogonadotropic hypogonadism phenotype in patients with Prader-Willi syndrome.
Aim: To investigate necdin gene (NDN) variants in patients with isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH).
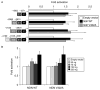
Patients and methods: We studied 160 Brazilian patients with IHH, which includes 92 with Kallmann syndrome and 68 with normosmic IHH. Genomic DNA was extracted and the single NDN exon was amplified and sequenced. To measure GNRH transcriptional activity, luciferase reporter plasmids containing GNRH regulatory regions were transiently transfected into GT1-7 cells in the presence and absence of overexpressed wild-type or mutant necdin.
Results: A heterozygous variant of necdin, p.V318A, was identified in a 23-year-old male with Kallmann syndrome. The p.V318A was also present in affected aunt and his father and was absent in 100 Brazilian control subjects. Previous FGFR1 gene analysis revealed a missense mutation (p.P366L) in this family. Functional studies revealed a minor difference in the activation of GNRH transcription by mutant protein compared with wild type in that a significant impairment of the necdin protein activity threshold was observed.
Conclusion: A rare variant of necdin (p.V318A) was described in a family with Kallmann syndrome associated with a FGFR1 mutation. Familial segregation and in vitro analysis suggested that this non-synonymous variant did not have a direct causative role in the hypogonadism phenotype. NDN mutations are not a frequent cause of congenital IHH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures

References
-
- Pitteloud N, Quinton R, Pearce S, Raivio T, Acierno J, Dwyer A, Plummer L, Hughes V, Seminara S, Cheng YZ, Li WP, Maccoll G, Eliseenkova AV, Olsen SK, Ibrahimi OA, Hayes FJ, Boepple P, Hall JE, Bouloux P, Mohammadi M, Crowley W. Digenic mutations account for variable phenotypes in idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2007;117:457–463. doi: 10.1172/JCI29884. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto S, Yamazaki C, Masumoto KH, Nagano M, Naito M, Soga T, Hiyama H, Matsumoto M, Takasaki J, Kamohara M, Matsuo A, Ishii H, Kobori M, Katoh M, Matsushime H, Furuichi K, Shigeyoshi Y. Abnormal development of the olfactory bulb and reproductive system in mice lacking prokineticin receptor PKR2. PNAS. 2006;103:4140–4145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.050 8881103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim HG, Kurth I, Lan F, Meliciani I, Wenzel W, Eom SH, Kang GB, Rosenberger G, Tekin M, Ozata M, Bick DP, Sherins RJ, Walker SL, Shi Y, Gusella JF, Layman LC. Mutations in CHD7, encoding a chromatin-remodeling protein, cause idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and Kallmann syndrome. American Journal of Human Genetics. 2008;83:511–519. doi: 10. 1016/j.ajhg.2008.09.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

