Determination of serum and plasma sclerostin concentrations by enzyme-linked immunoassays
- PMID: 21543425
- PMCID: PMC3135202
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2011-0254
Determination of serum and plasma sclerostin concentrations by enzyme-linked immunoassays
Abstract
Background: Sclerostin alters bone formation. The precise and reproducible measurement of sclerostin concentrations in biological samples is important for assessment of metabolic bone disease. We determined sclerostin concentrations in serum and plasma using two commercially available ELISA.
Methods: We measured sclerostin concentrations in serum or heparin-plasma obtained from 25 normal human subjects using two commercial ELISA available from Biomedica Medizinprodukte GmbH and TECOmedical AG.
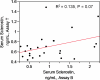
Results: With the Biomedica assay, serum sclerostin concentrations were 0.99 ± 0.12 ng/ml (mean ± sem), and plasma concentrations were 1.47 ± 0.13 ng/ml (paired t test, P < 0.001). With the TECO assay, serum sclerostin levels were 0.71 ± 0.05 ng/ml, and plasma sclerostin concentrations were 0.80 ± 0.06 ng/ml (paired t test, P < 0.001). Serum and plasma sclerostin concentrations were significantly different when determined by the two assays (serum, P = 0.015; plasma, P < 0.001). Recovery of added recombinant sclerostin to serum was less than expected with both Biomedica and TECO assays (P < 0.001, paired t test).
Conclusions: The concentrations of sclerostin in serum and plasma are different when determined by the two assays. Serum or plasma sclerostin concentrations with current assays should be interpreted with caution. The data suggest that the same assay should be used for comparing groups of patients or patients being followed longitudinally. Standardization of sclerostin assays is required before being introduced into general clinical laboratory use.
Figures
References
-
- Li X, Zhang Y, Kang H, Liu W, Liu P, Zhang J, Harris SE, Wu D. 2005. Sclerostin binds to LRP5/6 and antagonizes canonical Wnt signaling. J Biol Chem 280:19883–19887 - PubMed
-
- ten Dijke P, Krause C, de Gorter DJ, Lowik CW, van Bezooijen RL. 2008. Osteocyte-derived sclerostin inhibits bone formation: its role in bone morphogenetic protein and Wnt signaling. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(Suppl 1):31–35 - PubMed
-
- Balemans W, Piters E, Cleiren E, Ai M, Van Wesenbeeck L, Warman ML, Van Hul W. 2008. The binding between sclerostin and LRP5 is altered by DKK1 and by high-bone mass LRP5 mutations. Calcified tissue international 82:445–453 - PubMed
-
- Lin C, Jiang X, Dai Z, Guo X, Weng T, Wang J, Li Y, Feng G, Gao X, He L. 2009. Sclerostin mediates bone response to mechanical unloading through antagonizing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Bone Miner Res 24:1651–1661 - PubMed
-
- Winkler DG, Sutherland MS, Ojala E, Turcott E, Geoghegan JC, Shpektor D, Skonier JE, Yu C, Latham JA. 2005. Sclerostin inhibition of Wnt-3a-induced C3H10T1/2 cell differentiation is indirect and mediated by bone morphogenetic proteins. J Biol Chem 280:2498–2502 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources