Role of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses against JC virus in the outcome of patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) and PML with immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome
- PMID: 21543472
- PMCID: PMC3126613
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02506-10
Role of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses against JC virus in the outcome of patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) and PML with immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome
Abstract
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a severe demyelinating disease of the brain caused by JC virus (JCV). To assess the role of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cells against JCV in the clinical outcome of PML and PML in the setting of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS), we tested gamma interferon (IFN-γ) response by enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot (ELISpot) and intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) in 117 subjects, including 66 PML patients with different clinical outcomes. Both assays were concordant and demonstrated that the cellular immune response against JCV is associated with better clinical outcome. PML survivors had an early CD8(+) T-cell response more frequently than PML progressors (100% versus 27.3%; P = 0.001), while only a trend was observed for the early CD4(+) T-cell response between these two groups (80% versus 45.5%; P = 0.18). Although IRIS itself was more frequent in the PML survivor group, there was no difference in IFN-γ-producing CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cells between IRIS and non-IRIS PML patients, suggesting that T-cells expressing other cytokines likely have a role in the immunopathogenesis of IRIS. ELISpot and ICS assays are useful prognostic markers of PML evolution and may help in the clinical management of these patients.
Figures


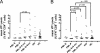
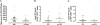
References
-
- Bourgarit A., et al. 2006. Explosion of tuberculin-specific Th1-responses induces immune restoration syndrome in tuberculosis and HIV co-infected patients. AIDS 20:F1–F7 - PubMed
-
- Cianchetta-Sivori M., Raso S., Fernandez-Guerrero M., Gorgolas M., Garcia R. 2007. Do CD8(+)CD25(+) cells predict immune reconstitution syndrome in HIV-positive patients who begin HAART? AIDS 21:2347–2349 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- T32 AI007387/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 NS 060950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS041198/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS 041198/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS 047029/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR 025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI060354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA09031-32/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI60354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009031/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047029/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 NS060950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

