Sensitive and specific phenotypic assay for metallo-beta-lactamase detection in Enterobacteria by use of a moxalactam disk supplemented with EDTA
- PMID: 21543570
- PMCID: PMC3147818
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00328-11
Sensitive and specific phenotypic assay for metallo-beta-lactamase detection in Enterobacteria by use of a moxalactam disk supplemented with EDTA
Abstract
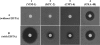
Moxalactam is highly hydrolyzed by plasmid-mediated metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs), whereas it is poorly inactivated by serine-active carbapenemases. This study demonstrated that moxalactam resistance constituted an effective screen for MBL expression in enterobacteria, which could be confirmed, even in low-MBL-producing isolates, by a disk potentiation test using moxalactam and EDTA.
Figures
References
-
- Cao V. T. B. C., et al. 2000. Emergence of imipenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae owing to combination of plasmid-mediated CMY-4 and permeability alteration. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 46:895–900 - PubMed
-
- Chu Y. W., Cheung T. K., Ngan J. Y., Kam K. M. 2005. EDTA susceptibility leading to false detection of metallo-β-lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Etest and an imipenem-EDTA disk method. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 26:340–341 - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2010. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 20th informational supplement. Approved standard M100-S20. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute June 2010. update. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 20th informational supplement. Approved standard M100-S20-U. CLSI, Wayne, PA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

