AP-1 protein induction during monopoiesis favors C/EBP: AP-1 heterodimers over C/EBP homodimerization and stimulates FosB transcription
- PMID: 21543584
- PMCID: PMC3177697
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0111043
AP-1 protein induction during monopoiesis favors C/EBP: AP-1 heterodimers over C/EBP homodimerization and stimulates FosB transcription
Abstract
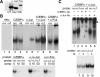
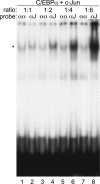
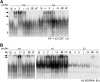
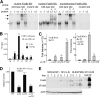
AP-1 proteins heterodimerize via their LZ domains to bind TGACGTCA or TGACTCA, whereas C/EBPs dimerize to bind ATTGCGCAAT. We demonstrate that intact C/EBPα also heterodimerizes with c-Jun or c-Fos to bind a hybrid DNA element, TGACGCAA, or more weakly to TGATGCAA. A 2:1 ratio of c-Jun:C/EBPα or c-Fos:C/EBPα was sufficient for preferential binding. Semiquantitative Western blot analysis indicates that the summation of c-Jun, JunB, and c-Fos levels in differentiating myeloid cells is similar to or exceeds the entirety of C/EBPα and C/EBPβ, indicating the feasibility of heterodimer formation. Induction of AP-1 proteins during monocytic differentiation favored formation of C/EBP:AP-1 heterodimers, with C/EBPα homodimers more evident during granulopoiesis. Approximately 350 human and 300 murine genes contain the TGACGCAA motif between -2 kb and +1 kb of their transcription start sites. We focused on the murine Fosb promoter, which contains a C/EBP:AP-1 cis element at -56 and -253, with the hFOSB gene containing an identical site at -253 and a 1-bp mismatch at -56. C/EBPα:AP-1 heterodimers bound either site preferentially in a gel-shift assay, C/EBPα:c-Fos ER fusion proteins induced endogenous Fosb mRNA but not in the presence of CHX, C/EBP and AP-1 proteins bound the endogenous Fosb promoter, mutation of the -56 cis element reduced reporter activity fivefold, and endogenous FosB protein was expressed preferentially during monopoiesis versus granulopoiesis. Increased expression of Jun/Fos proteins elevates C/EBP:AP-1 heterodimer formation to potentially activate novel sets of genes during monopoiesis and potentially during other biologic processes.
Figures



Comment in
-
Editorial: granulopoiesis versus monopoiesis: a consequence of transcription factors dancing with the right partners.J Leukoc Biol. 2011 Oct;90(4):637-8. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0411187. J Leukoc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21965310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. (1989) The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science 243, 1681–1688 - PubMed
-
- Miller M., Shuman J. D., Sebastian T., Dauter Z., Johnson P. F. (2003) Structural basis for DNA recognition by the basic region leucine zipper transcription factor C/EBPα. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 15178–15184 - PubMed
-
- Mechta-Grigoriou F., Gerald D., Yaniv M. (2001) The mammalian Jun proteins: redundancy and specificity. Oncogene 20, 2378–2389 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

