A functional role for Nlrp6 in intestinal inflammation and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 21543645
- PMCID: PMC3133458
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100412
A functional role for Nlrp6 in intestinal inflammation and tumorigenesis
Abstract
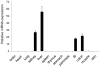
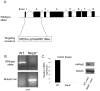
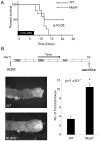
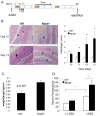
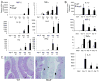
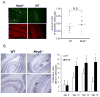
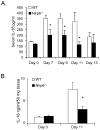
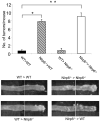
The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor (NLR) family member, Nlrp6, has been implicated in inflammasome signaling to activate caspase-1, which is essential for the production of mature IL-1β and IL-18. However, a function for Nlrp6 in vivo has never been demonstrated. Due to the relative high expression of Nlrp6 in intestinal tissue, we hypothesized that Nlrp6 has a role in intestinal homeostasis. Indeed, Nlrp6-deficient mice are more susceptible to chemically induced colitis as well as colitis-induced tumorigenesis than wild-type (WT) mice. Nlrp6-deficient mice exhibited significantly more inflammation within the colon than WT mice after dextran sulfate sodium treatment. Their inability to resolve inflammation and repair damaged epithelium as efficiently as WT mice resulted in prolonged increases in epithelial proliferative activity that likely underlie the increased propensity for tumors in these mice during chronic inflammation. We further show that the activity of Nlrp6 in hematopoietic cells is critical for protection against inflammation-related colon tumorigenesis. This study highlights the importance of NLR function in maintaining intestinal homeostasis to prevent the development of aberrant inflammation and tumor development within the colon.
Figures
References
-
- Chen G, Shaw MH, Kim YG, Nunez G. NOD-like receptors: role in innate immunity and inflammatory disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2009;4:365–398. - PubMed
-
- Bouskra D, Brezillon C, Berard M, Werts C, Varona R, Boneca IG, Eberl G. Lymphoid tissue genesis induced by commensals through NOD1 regulates intestinal homeostasis. Nature. 2008;456:507–510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

