Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7)-driven accumulation of a novel CD11c⁺ B-cell population is important for the development of autoimmunity
- PMID: 21543762
- PMCID: PMC3152497
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-331462
Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7)-driven accumulation of a novel CD11c⁺ B-cell population is important for the development of autoimmunity
Abstract
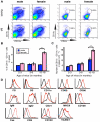
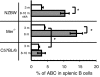
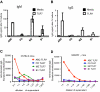
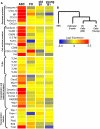
Females are more susceptible than males to many autoimmune diseases. The processes causing this phenomenon are incompletely understood. Here, we demonstrate that aged female mice acquire a previously uncharacterized population of B cells that we call age-associated B cells (ABCs) and that these cells express integrin α(X) chain (CD11c). This unexpected population also appears in young lupus-prone mice. On stimulation, CD11c(+) B cells, both from autoimmune-prone and healthy strains of mice, secrete autoantibodies, and depletion of these cells in vivo leads to reduction of autoreactive antibodies, suggesting that the cells might have a direct role in the development of autoimmunity. We have explored factors that contribute to appearance of ABCs and demonstrated that signaling through Toll-like receptor 7 is crucial for development of this B cell population. We were able to detect a similar population of B cells in the peripheral blood of some elderly women with autoimmune disease, suggesting that there may be parallels between the creation of ABC-like cells between mice and humans.
Figures
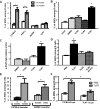
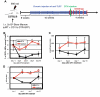

Comment in
-
Now you know your ABCs.Blood. 2011 Aug 4;118(5):1187-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-06-355131. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21816835 No abstract available.
References
-
- Beeson PB. Age and sex associations of 40 autoimmune diseases. Am J Med. 1994;96(5):457–462. - PubMed
-
- Whitacre CC. Sex differences in autoimmune disease. Nat Immunol. 2001;2(9):777–780. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy LG, Will R, Calin A. Sex ratio in the spondyloarthropathies and its relationship to phenotypic expression, mode of inheritance and age at onset. J Rheumatol. 1993;20(11):1900–1904. - PubMed
-
- Gubbels Bupp MR, Jorgensen TN, Kotzin BL. Identification of candidate genes that influence sex hormone-dependent disease phenotypes in mouse lupus. Genes Immun. 2008;9(1):47–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

