The inducible deletion of Drosha and microRNAs in mature podocytes results in a collapsing glomerulopathy
- PMID: 21544061
- PMCID: PMC3246347
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2011.122
The inducible deletion of Drosha and microRNAs in mature podocytes results in a collapsing glomerulopathy
Abstract
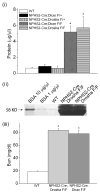
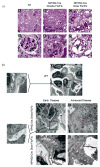
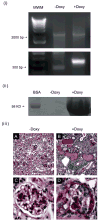
Micro-RNAs (miRNAs) are short (average 22 nucleotides) noncoding regulatory RNAs that inhibit gene expression by targeting complementary 3'-untranslated regions of protein-encoding mRNAs for translational repression or degradation. miRNAs play key roles in both the function and differentiation of many cell types. Drosha and Dicer, two RNAase III enzymes, function in a stepwise manner to generate a mature miRNA. Previous studies have shown that podocyte-specific deletion of Dicer during development results in proteinuric renal disease and collapsing glomerulopathy (CG); however, Dicer has functions other than the generation of miRNAs. Here we found that the podocyte-specific deletion of Drosha results in a similar phenotype to Dicer mutants, confirming that the Dicer mutant phenotype is due to the loss of miRNAs. Moreover, the inducible deletion of Drosha in 2- to 3-month-old mice (Tet-On system) resulted in CG. Thus, continuous generation of miRNAs are required for the normal function of mature podocytes and their loss leads to CG. Identifying these miRNAs may provide new insight into disease pathogenesis and novel therapeutic targets in various podocytopathies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Comment in
-
The next level of complexity: post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs.Kidney Int. 2011 Oct;80(7):692-3. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.175. Kidney Int. 2011. PMID: 21918556
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Rana TM. Illuminating the silence: understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:23–36. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:102–114. - PubMed
-
- Eulalio A, Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E. Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell. 2008;132:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J, et al. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature. 2003;425:415–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

