Fast parallel tandem mass spectral library searching using GPU hardware acceleration
- PMID: 21545112
- PMCID: PMC3107871
- DOI: 10.1021/pr200074h
Fast parallel tandem mass spectral library searching using GPU hardware acceleration
Abstract
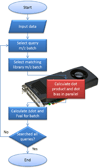
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics is a maturing discipline of biologic research that is experiencing substantial growth. Instrumentation has steadily improved over time with the advent of faster and more sensitive instruments collecting ever larger data files. Consequently, the computational process of matching a peptide fragmentation pattern to its sequence, traditionally accomplished by sequence database searching and more recently also by spectral library searching, has become a bottleneck in many mass spectrometry experiments. In both of these methods, the main rate-limiting step is the comparison of an acquired spectrum with all potential matches from a spectral library or sequence database. This is a highly parallelizable process because the core computational element can be represented as a simple but arithmetically intense multiplication of two vectors. In this paper, we present a proof of concept project taking advantage of the massively parallel computing available on graphics processing units (GPUs) to distribute and accelerate the process of spectral assignment using spectral library searching. This program, which we have named FastPaSS (for Fast Parallelized Spectral Searching), is implemented in CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) from NVIDIA, which allows direct access to the processors in an NVIDIA GPU. Our efforts demonstrate the feasibility of GPU computing for spectral assignment, through implementation of the validated spectral searching algorithm SpectraST in the CUDA environment.
Figures

References
-
- Yates JR, Ruse CI, Nakorchevsky A. Proteomics by mass spectrometry: approaches, advances, and applications. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2009;11:49–79. - PubMed
-
- Kapp E, Schutz F. Overview of tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) database search algorithms. Curr Protoc Protein Sci. 2007;Chapter 25(Unit25):2. - PubMed
-
- Nesvizhskii AI. Protein identification by tandem mass spectrometry and sequence database searching. Methods Mol Biol. 2007;367:87–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

