Xylem structure of four grape varieties and 12 alternative hosts to the xylem-limited bacterium Xylella fastidious
- PMID: 21546428
- PMCID: PMC3119617
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcr106
Xylem structure of four grape varieties and 12 alternative hosts to the xylem-limited bacterium Xylella fastidious
Abstract
Background and aims: The bacterium Xylella fastidiosa (Xf), responsible for Pierce's disease (PD) of grapevine, colonizes the xylem conduits of vines, ultimately killing the plant. However, Vitis vinifera grapevine varieties differ in their susceptibility to Xf and numerous other plant species tolerate Xf populations without showing symptoms. The aim of this study was to examine the xylem structure of grapevines with different susceptibilities to Xf infection, as well as the xylem structure of non-grape plant species that support or limit movement of Xf to determine if anatomical differences might explain some of the differences in susceptibility to Xf.
Methods: Air and paint were introduced into leaves and stems to examine the connectivity between stem and leaves and the length distribution of their vessels. Leaf petiole and stem anatomies were studied to determine the basis for the free or restricted movement of Xf into the plant.
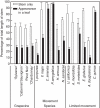
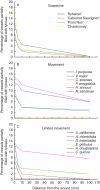
Key results: There were no obvious differences in stem or petiole vascular anatomy among the grape varieties examined, nor among the other plant species that would explain differences in resistance to Xf. Among grape varieties, the more tolerant 'Sylvaner' had smaller stem vessel diameters and 20 % more parenchyma rays than the other three varieties. Alternative hosts supporting Xf movement had slightly longer open xylem conduits within leaves, and more connection between stem and leaves, when compared with alternative hosts that limit Xf movement.
Conclusions: Stem--leaf connectivity via open xylem conduits and vessel length is not responsible for differences in PD tolerance among grape varieties, or for limiting bacterial movement in the tolerant plant species. However, it was found that tolerant host plants had narrower vessels and more parenchyma rays, possibly restricting bacterial movement at the level of the vessels. The implications of xylem structure and connectivity for the means and regulation of bacterial movement are discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Aloni R, Griffith M. Functional xylem anatomy in root–shoot junctions of six cereal species. Planta. 1991;184:123–129. - PubMed
-
- Alves E, Marucci CR, Lopes JRS, Leite B. Leaf symptoms on plum, coffee and citrus and the relationship with the extent of xylem vessels colonized by Xylella fastidiosa. Journal of Phytopathology. 2004;152:291–297.
-
- André JP. Organisation vasculaire des angiospermes: une vision nouvelle. Paris: Institut Nationale de la Recherche Agronomique (INRA); 2002.
-
- André JP, Catesson AM, Liberman M. Characters and origin of vessels with heterogenous structure in leaf and flower abscission zones. Canadian Journal of Botany. 1999;77:253–261.

