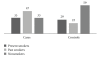Family history of cancer and tobacco exposure in index cases of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 21547248
- PMCID: PMC3085295
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/215985
Family history of cancer and tobacco exposure in index cases of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Aim. To examine interaction between history of cancer in first-degree relatives and tobacco smoking in index patients of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Methods. We carried out a case-control involving 113 patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and 110 controls over a 12-month period at the Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK. They were all administered a detailed tobacco exposure questionnaire and a family history questionnaire. We calculated cumulative tobacco exposure and risk for pancreas cancer. Results. Both smokers (OR 3.01 (95% CI: 1.73 to 5.24)) and those with a family history of malignancy (OR 1.98 (95% CI: 1.15-3.38)) were more likely to develop pancreatic cancer. Having more than one first-degree relative with cancer did not significantly further increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. Amongst pancreatic cancer cases, cumulative tobacco exposure was significantly decreased (P = .032) in the group of smokers (current and ex-smokers) who had a family history of malignancy [mean (SD): 30.00 (24.77) pack-years versus 44.69 (28.47) pack-years with no such history]. Conclusions. Individuals with a family history of malignancy are at an increased risk of pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, individuals with a family history of malignancy and who smoke appear to require a lesser degree of tobacco exposure for the development of pancreatic cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pancreatic Cancer Risk in Relation to Lifetime Smoking Patterns, Tobacco Type, and Dose-Response Relationships.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2020 May;29(5):1009-1018. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-19-1027. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2020. PMID: 32051190
-
Association between self-reported environmental tobacco smoke exposure and lung cancer: modification by GSTP1 polymorphism.Int J Cancer. 2003 May 10;104(6):758-63. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10989. Int J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12640684
-
Environmental tobacco smoke and the risk of pancreatic cancer: findings from a Canadian population-based case-control study.Can J Public Health. 2004 Jan-Feb;95(1):32-7. doi: 10.1007/BF03403631. Can J Public Health. 2004. PMID: 14768739 Free PMC article.
-
Aspects of the epidemiology of lung cancer in smokers and nonsmokers in the United States.Lung Cancer. 1996 Aug;15(1):1-20. doi: 10.1016/0169-5002(95)00566-8. Lung Cancer. 1996. PMID: 8865119 Review.
-
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Epidemiology and Risk Factors.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Mar 20;11(3):562. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11030562. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hereditary pancreatic cancer: molecular bases and their application in diagnosis and clinical management: a guideline of the TTD group.Clin Transl Oncol. 2012 Aug;14(8):553-63. doi: 10.1007/s12094-012-0840-0. Epub 2012 Jul 19. Clin Transl Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22855135 Review.
-
Sleep duration and the risk of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis including dose-response relationship.BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 21;18(1):1149. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5025-y. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30463535 Free PMC article.
-
The complexities of epidemiology and prevention of gastrointestinal cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Oct 1;13(10):12556-72. doi: 10.3390/ijms131012556. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23202913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms based genetic risk score in the prediction of pancreatic cancer risk.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jun 14;26(22):3076-3086. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3076. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32587449 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hammond EC. Smoking in relation to mortality and morbidity. Findings in first thirty-four months of follow-up in a prospective study started in 1959. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1964;32:1161–1188. - PubMed
-
- Li D, Xie K, Wolff R, Abbruzzese JL. Pancreatic cancer. The Lancet. 2004;363(9414):1049–1057. - PubMed
-
- Petersen GM, De Andrade M, Goggins M, et al. Pancreatic cancer genetic epidemiology consortium. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention. 2006;15(4):704–710. - PubMed
-
- Earl J, Yan LI, Vitone LJ, et al. Evaluation of the 4q32-34 locus in European familial pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention. 2006;15(10):1948–1955. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources