The pharmacological effects of the thermostabilising (m23) mutations and intra and extracellular (β36) deletions essential for crystallisation of the turkey β-adrenoceptor
- PMID: 21547538
- PMCID: PMC3116118
- DOI: 10.1007/s00210-011-0648-4
The pharmacological effects of the thermostabilising (m23) mutations and intra and extracellular (β36) deletions essential for crystallisation of the turkey β-adrenoceptor
Abstract
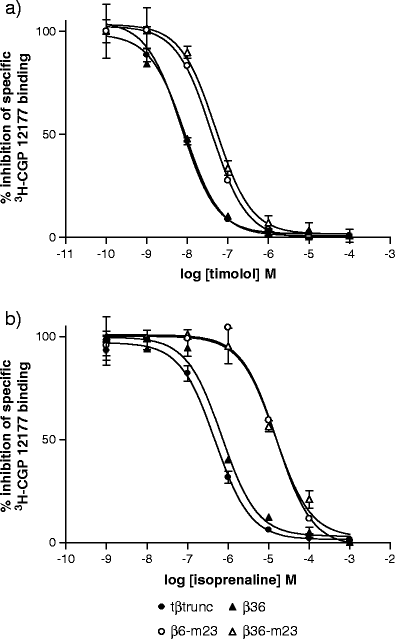
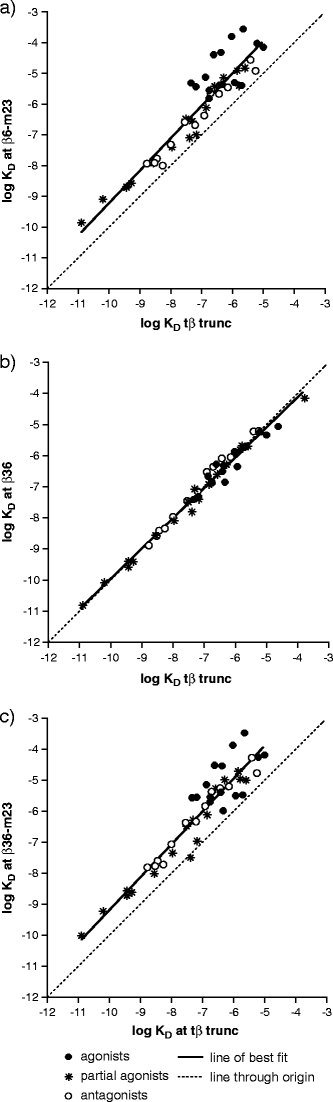
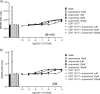
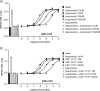
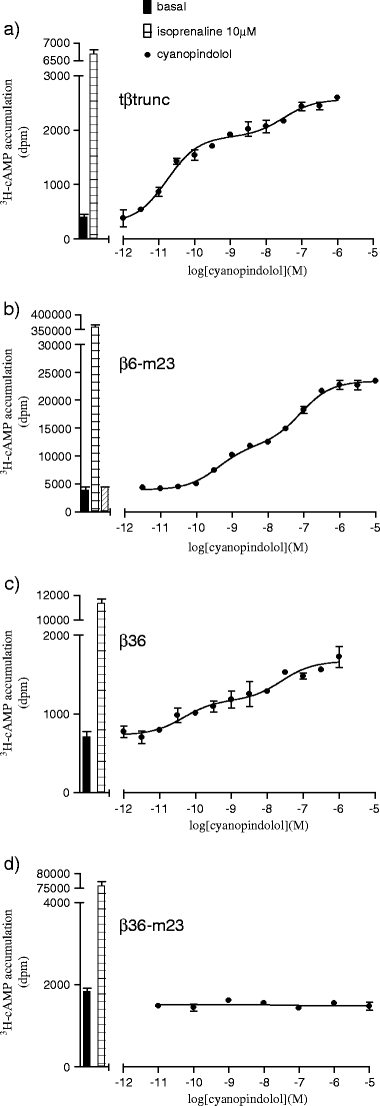
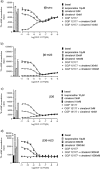
The X-ray crystal structure of the turkey β-adrenoceptor has recently been determined. However, mutations were introduced into the native receptor that was essential for structure determination. These may cause alterations to the receptor pharmacology. It is therefore essential to understand the effects of these mutations on the pharmacological characteristics of the receptor. This study examined the pharmacological effects of both the m23 mutations and the β36 deletions, both alone and then in combination in the β36-m23 mutant used in the crystallisation and structure determination of the turkey β-adrenoceptor. Stable CHO-K1 cell lines were made of each of the receptor mutants and the affinity and efficacy of ligands assessed by (3)H-CGP 12177 whole cell ligand binding, (3)H-cAMP accumulation, and CRE-SPAP gene transcription assays. The m23 mutations reduced affinity for agonists, partial agonists and neutral antagonists by about tenfold whilst the β36 deletions alone had no effect on ligand affinity. Both sets of changes appeared to reduce the agonist activation of the receptor. Both the m23 and the β36 receptors retained two active agonist-induced receptor conformations similar to that of the original tβtrunc receptor. The combined β36-m23 receptor bound ligands with similar affinity to the m23 receptor; however, agonist activation was only observed with a few agonists including the catecholamines. Although the combination of mutations severely reduced the activation ability, the final crystallised receptor (β36-m23) was still a fully functional receptor capable of binding agonist and antagonist ligands and activating intracellular agonist responses.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

