In situ forming poly(ethylene glycol)-based hydrogels via thiol-maleimide Michael-type addition
- PMID: 21548071
- PMCID: PMC4529490
- DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.33106
In situ forming poly(ethylene glycol)-based hydrogels via thiol-maleimide Michael-type addition
Abstract
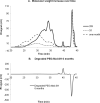
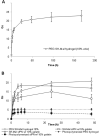
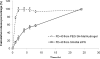
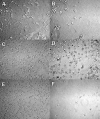
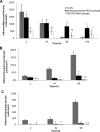
The incorporation of cells and sensitive compounds can be better facilitated without the presence of UV or other energy sources that are common in the formation of biomedical hydrogels such as poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels. The formation of hydrogels by the step-growth polymerization of maleimide- and thiol-terminated poly(ethylene glycol) macromers via Michael-type addition is described. The effects of macromer concentration, pH, temperature, and the presence of biomolecule gelatin on gel formation were investigated. Reaction kinetics between maleimide and thiol functional groups were found to be rapid. Molecular weight increase over time was characterized via gel permeation chromatography during step-growth polymerization. Swelling and degradation results showed incorporating gelatin enhanced swelling and accelerated degradation. Increasing gelatin content resulted in the decreased storage modulus (G'). The in vitro release kinetics of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled dextran from the resulting matrices demonstrated the potential in the development of novel in situ gel-forming drug delivery systems. Moreover, the resulting networks were minimally adhesive to primary human monocytes, fibroblasts, and keratinocytes thus providing an ideal platform for further biofunctionalizations to direct specific biological response.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
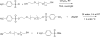
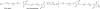
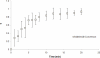


References
-
- Nguyen KT, West JL. Photopolymerizable hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials. 2002;23:4307–4314. - PubMed
-
- Wang ZC, Xu XD, Chen CS, Yun L, Song JC, Zhang XZ, Zhuo RX. In situ formation of thermosensitive PNIPAAm-based hydrogels by Michael-type addition reaction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2010;2:1009–1018. - PubMed
-
- Bae SJ, Suh JM, Sohn YS, Bae YH, Kim SW, Jeong B. Thermogelling poly(caprolactone-bethylene glycol-b-caprolactone) aqueous solutions. Macromolecules. 2005;38:5260–5265.
-
- Mather BD, Wiswanathan K, Miller KM, Long TE. Michael addition reactions in macromolecular design for emerging technologies. Prog Polym Sci. 2006;31:487–531.
-
- Chan JW, Hoyle CE, Lowe AB, Bowman M. Nucleophile-initiated thiol-Michael reactions: effect of organocatalyst, thiol, and ene. Macromolecules. 2010;43:6381–6388.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

