Concurrent androgen deprivation therapy during salvage prostate radiotherapy improves treatment outcomes in high-risk patients
- PMID: 21549519
- PMCID: PMC3904219
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.08.030
Concurrent androgen deprivation therapy during salvage prostate radiotherapy improves treatment outcomes in high-risk patients
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether concurrent androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) during salvage radiotherapy (RT) improves prostate cancer treatment outcomes.
Methods and materials: A total of 630 postprostatectomy patients were retrospectively identified who were treated with three-dimensional conformal RT. Of these, 441 were found to be treated for salvage indications. Biochemical failure was defined as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) of 0.2 ng/mL or greater above nadir with another PSA increase or the initiation of salvage ADT. Progression-free survival (PFS) was defined as the absence of biochemical failure, continued PSA rise despite salvage therapy, initiation of systemic therapy, clinical progression, or distant failure. Multivariate-adjusted Cox proportional hazards modeling was performed to determine which factors predict PFS.
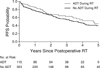
Results: Low-, intermediate-, and high-risk patients made up 10%, 24%, and 66% of patients, respectively. The mean RT dose was 68 Gy. Twenty-four percent of patients received concurrent ADT (cADT). Regional pelvic nodes were treated in 16% of patients. With a median follow-up of 3 years, the 3-year PFS was 4.0 years for cADT vs. 3.4 years for cADT patients (p = 0.22). Multivariate analysis showed that concurrent ADT (p = 0.05), Gleason score (p < 0.001), and pre-RT PSA (p = 0.03) were independent predictors of PFS. When patients were stratified by risk group, the benefits of cADT (hazard ratio, 0.65; p = 0.046) were significant only for high-risk patients.
Conclusions: This retrospective study showed a PFS benefit of concurrent ADT during salvage prostate RT. This benefit was observed only in high-risk patients.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Han M, Partin AW, Pound CR, Epstein JI, Walsh PC. Long-term biochemical disease-free and cancer-specific survival following anatomic radical retropubic prostatectomy. The 15-year Johns Hopkins experience. Urol Clin North Am. 2001;28:555–565. - PubMed
-
- Roehl KA, Han M, Ramos CG, Antenor JA, Catalona WJ. Cancer progression and survival rates following anatomical radical retropubic prostatectomy in 3,478 consecutive patients: long-term results. J Urol. 2004;172:910–914. - PubMed
-
- Suardi N, Porter CR, Reuther AM, Walz J, Kodama K, Gibbons RP, Correa R, Montorsi F, Graefen M, Huland H, et al. A nomogram predicting long-term biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Cancer. 2008;112:1254–1263. - PubMed
-
- Pound CR, Partin AW, Eisenberger MA, Chan DW, Pearson JD, Walsh PC. Natural history of progression after PSA elevation following radical prostatectomy. Jama. 1999;281:1591–1597. - PubMed
-
- Freedland SJ, Humphreys EB, Mangold LA, Eisenberger M, Dorey FJ, Walsh PC, Partin AW. Risk of prostate cancer-specific mortality following biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Jama. 2005;294:433–439. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous