Evolution of abscisic acid synthesis and signaling mechanisms
- PMID: 21549957
- PMCID: PMC3119208
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.03.015
Evolution of abscisic acid synthesis and signaling mechanisms
Abstract
The plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) mediates seed dormancy, controls seedling development and triggers tolerance to abiotic stresses, including drought. Core ABA signaling components consist of a recently identified group of ABA receptor proteins of the PYRABACTIN RESISTANCE (PYR)/REGULATORY COMPONENT OF ABA RECEPTOR (RCAR) family that act as negative regulators of members of the PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE 2C (PP2C) family. Inhibition of PP2C activity enables activation of SNF1-RELATED KINASE 2 (SnRK2) protein kinases, which target downstream components, including transcription factors, ion channels and NADPH oxidases. These and other components form a complex ABA signaling network. Here, an in depth analysis of the evolution of components in this ABA signaling network shows that (i) PYR/RCAR ABA receptor and ABF-type transcription factor families arose during land colonization of plants and are not found in algae and other species, (ii) ABA biosynthesis enzymes have evolved to plant- and fungal-specific forms, leading to different ABA synthesis pathways, (iii) existing stress signaling components, including PP2C phosphatases and SnRK kinases, were adapted for novel roles in this plant-specific network to respond to water limitation. In addition, evolutionarily conserved secondary structures in the PYR/RCAR ABA receptor family are visualized.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
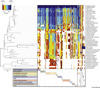

Comment in
-
Plant signalling pathways: a comparative evolutionary overview.Curr Biol. 2011 May 10;21(9):R317-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.04.013. Curr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21549953 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hartung W. The evolution of abscisic acid (ABA) and ABA function in lower plants, fungi and lichen. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010;37:806–812.
-
- Finkelstein R, Reeves W, Ariizumi T, Steber C. Molecular aspects of seed dormancy. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008;59:387–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

