Scaffold proteins: hubs for controlling the flow of cellular information
- PMID: 21551057
- PMCID: PMC3117218
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1198701
Scaffold proteins: hubs for controlling the flow of cellular information
Abstract
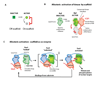
The spatial and temporal organization of molecules within a cell is critical for coordinating the many distinct activities carried out by the cell. In an increasing number of biological signaling processes, scaffold proteins have been found to play a central role in physically assembling the relevant molecular components. Although most scaffolds use a simple tethering mechanism to increase the efficiency of interaction between individual partner molecules, these proteins can also exert complex allosteric control over their partners and are themselves the target of regulation. Scaffold proteins offer a simple, flexible strategy for regulating selectivity in pathways, shaping output behaviors, and achieving new responses from preexisting signaling components. As a result, scaffold proteins have been exploited by evolution, pathogens, and cellular engineers to reshape cellular behavior.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

