The two actin-interacting protein 1 genes have overlapping and essential function for embryonic development in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 21551072
- PMCID: PMC3128528
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-12-0934
The two actin-interacting protein 1 genes have overlapping and essential function for embryonic development in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
Disassembly of actin filaments by actin-depolymerizing factor (ADF)/cofilin and actin-interacting protein 1 (AIP1) is a conserved mechanism to promote reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. We previously reported that unc-78, an AIP1 gene in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, is required for organized assembly of sarcomeric actin filaments in the body wall muscle. unc-78 functions in larval and adult muscle, and an unc-78-null mutant is homozygous viable and shows only weak phenotypes in embryos. Here we report that a second AIP1 gene, aipl-1 (AIP1-like gene-1), has overlapping function with unc-78, and that depletion of the two AIP1 isoforms causes embryonic lethality. A single aipl-1-null mutation did not cause a detectable phenotype. However, depletion of both unc-78 and aipl-1 arrested development at late embryonic stages due to severe disorganization of sarcomeric actin filaments in body wall muscle. In vitro, both AIPL-1 and UNC-78 preferentially cooperated with UNC-60B, a muscle-specific ADF/cofilin isoform, in actin filament disassembly but not with UNC-60A, a nonmuscle ADF/cofilin. AIPL-1 is expressed in embryonic muscle, and forced expression of AIPL-1 in adult muscle compensated for the function of UNC-78. Thus our results suggest that enhancement of actin filament disassembly by ADF/cofilin and AIP1 proteins is critical for embryogenesis.
Figures

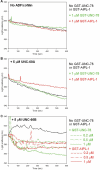
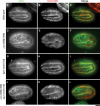
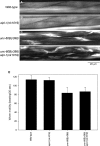
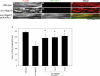
References
-
- Aizawa H, Katadae M, Maruya M, Sameshima M, Murakami-Murofushi K, Yahara I. Hyperosmotic stress-induced reorganization of actin bundles in Dictyostelium cells over-expressing cofilin. Genes Cells. 1999;4:311–324. - PubMed
-
- Andrianantoandro E, Pollard TD. Mechanism of actin filament turnover by severing and nucleation at different concentrations of ADF/cofilin. Mol Cell. 2006;24:13–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

