msl2 mRNA is bound by free nuclear MSL complex in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 21551218
- PMCID: PMC3159442
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr236
msl2 mRNA is bound by free nuclear MSL complex in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
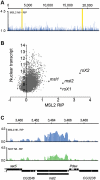
In Drosophila, the global increase in transcription from the male X chromosome to compensate for its monosomy is mediated by the male-specific lethal (MSL) complex consisting of five proteins and two non-coding RNAs, roX1 and roX2. After an initial sequence-dependent recognition by the MSL complex of 150-300 high affinity sites, the spread to the majority of the X-linked genes depends on local MSL-complex concentration and active transcription. We have explored whether any additional RNA species are associated with the MSL complex. No additional roX RNA species were found, but a strong association was found between a spliced and poly-adenylated msl2 RNA and the MSL complex. Based on our results, we propose a model in which a non-chromatin-associated partial or complete MSL-complex titrates newly transcribed msl2 mRNA and thus regulates the amount of available MSL complex by feedback. This represents a novel mechanism in chromatin structure regulation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Autoregulation of the Drosophila Noncoding roX1 RNA Gene.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(3):e1002564. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002564. Epub 2012 Mar 15. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22438819 Free PMC article.
-
roX RNAs are required for increased expression of X-linked genes in Drosophila melanogaster males.Genetics. 2006 Dec;174(4):1859-66. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.064568. Epub 2006 Oct 8. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 17028315 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporation of the noncoding roX RNAs alters the chromatin-binding specificity of the Drosophila MSL1/MSL2 complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Feb;28(4):1252-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00910-07. Epub 2007 Dec 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18086881 Free PMC article.
-
The right dose for every sex.Chromosoma. 2007 Apr;116(2):95-106. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0089-x. Epub 2006 Nov 24. Chromosoma. 2007. PMID: 17124606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Path to equality strewn with roX.Dev Biol. 2004 May 1;269(1):18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.01.039. Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15081354 Review.
Cited by
-
Study of the Role of Long Noncoding roX RNA in Maintaining of the Dosage Compensation Complex in Drosophila melanogaster.Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2023 Dec;513(Suppl 1):S8-S11. doi: 10.1134/S160767292370062X. Epub 2024 Jan 7. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2023. PMID: 38189885
-
Sequence signatures involved in targeting the Male-Specific Lethal complex to X-chromosomal genes in Drosophila melanogaster.BMC Genomics. 2012 Mar 19;13:97. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-97. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22424303 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding roX RNAs prevent the binding of the MSL-complex to heterochromatic regions.PLoS Genet. 2014 Dec 11;10(12):e1004865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004865. eCollection 2014 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25501352 Free PMC article.
-
High-Affinity Sites Form an Interaction Network to Facilitate Spreading of the MSL Complex across the X Chromosome in Drosophila.Mol Cell. 2015 Oct 1;60(1):146-62. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.08.024. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26431028 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitylation of the acetyltransferase MOF in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS One. 2017 May 16;12(5):e0177408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177408. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28510597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Larsson J, Meller VH. Dosage compensation, the origin and the afterlife of sex chromosomes. Chromosome Res. 2006;14:417–431. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen DK, Disteche CM. Dosage compensation of the active X chromosome in mammals. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:47–53. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Oliver B. Dosage compensation goes global. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2007;17:113–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

