NFBD1/MDC1 regulates Cav1 and Cav2 independently of DNA damage and p53
- PMID: 21551225
- PMCID: PMC3901581
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0317
NFBD1/MDC1 regulates Cav1 and Cav2 independently of DNA damage and p53
Abstract
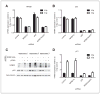
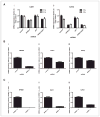
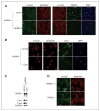
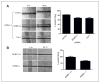
NFBD1/MDC1 is involved in DNA damage checkpoint signaling and DNA repair. NFBD1 binds to the chromatin component γH2AX at sites of DNA damage, causing amplification of ataxia telangiectasia-mutated gene (ATM) pathway signaling and recruitment of DNA repair factors. Residues 508-995 of NFBD1 possess transactivation activity, suggesting a possible role of NFBD1 in transcription. Furthermore, NFBD1 influences p53-mediated transcription in response to adriamycin. We sought to determine the role of NFBD1 in ionizing radiation (IR)-responsive transcription and if NFBD1 influences transcription independently of p53. Using microarray analysis, we identified genes altered upon NFBD1 knockdown. Surprisingly, most NFBD1 regulated genes are regulated in both the absence and presence of IR, thus pointing toward a novel function for NFBD1 outside of the DNA damage response. Furthermore, NFBD1 knockdown regulated genes mostly independent of p53 knockdown. These genes are involved in pathways including focal adhesion signaling, carbohydrate metabolism, and insulin signaling. We found that CAV1 and CAV2 mRNA and protein levels are reduced by both NFBD1 knockdown and knockout independently of IR and p53. NFBD1-depleted cells exhibit some similar phenotypes to Cav1-depleted cells. Furthermore, like Cav1-depletion, NFBD1 shRNA increases Erk phosphorylation. Thus, Cav1 could act as a mediator of the DNA-damage independent effects of NFBD1 in mitogenic signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
53BP1 and NFBD1/MDC1-Nbs1 function in parallel interacting pathways activating ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) in response to DNA damage.Cancer Res. 2003 Dec 15;63(24):8586-91. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14695167
-
NFBD1/MDC1, 53BP1 and BRCA1 have both redundant and unique roles in the ATM pathway.Cell Cycle. 2008 Nov 15;7(22):3584-94. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.22.7102. Epub 2008 Nov 29. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 19001859 Free PMC article.
-
NFBD1/Mdc1 mediates ATR-dependent DNA damage response.Cancer Res. 2005 Feb 15;65(4):1158-63. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2508. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15734998
-
Early events in the DNA damage response.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2004;63:1-35. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(04)63001-8. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15536012 Review.
-
The p53 response during DNA damage: impact of transcriptional cofactors.Biochem Soc Symp. 2006;(73):181-9. doi: 10.1042/bss0730181. Biochem Soc Symp. 2006. PMID: 16626298 Review.
Cited by
-
NFBD1/MDC1 is phosphorylated by PLK1 and controls G2/M transition through the regulation of a TOPOIIα-mediated decatenation checkpoint.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 11;8(12):e82744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082744. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349352 Free PMC article.
-
MDC1 functionally identified as an androgen receptor co-activator participates in suppression of prostate cancer.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 May 26;43(10):4893-908. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv394. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25934801 Free PMC article.
-
Proteogenomic analysis of Inhibitor of Differentiation 4 (ID4) in basal-like breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 11;22(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01306-6. Breast Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32527287 Free PMC article.
-
RPL24: a potential therapeutic target whose depletion or acetylation inhibits polysome assembly and cancer cell growth.Oncotarget. 2014 Jul 15;5(13):5165-76. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2099. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24970821 Free PMC article.
-
A Newfound association between MDC1 functional polymorphism and lung cancer risk in Chinese.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 8;9(9):e106794. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106794. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25198518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bork P, Hofmann K, Bucher P, Neuwald AF, Altschul SF, Koonin EV. A superfamily of conserved domains in DNA damage-responsive cell cycle checkpoint proteins. Faseb J. 1997;11:68–76. - PubMed
-
- Xu X, Stern DF. NFBD1/KIAA0170 is a chromatin-associated protein involved in DNA damage signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:8795–803. - PubMed
-
- Stewart GS, Wang B, Bignell CR, Taylor AM, Elledge SJ. MDC1 is a mediator of the mammalian DNA damage checkpoint. Nature. 2003;421:961–6. - PubMed
-
- Shang YL, Bodero AJ, Chen PL. NFBD1, a novel nuclear protein with signature motifs of FHA and BRCT, and an internal 41-amino acid repeat sequence, is an early participant in DNA damage response. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:6323–9. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg M, Stucki M, Falck J, D’Amours D, Rahman D, Pappin D, et al. MDC1 is required for the intra-S-phase DNA damage checkpoint. Nature. 2003;421:952–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

