Intraplantar-injected ceramide in rats induces hyperalgesia through an NF-κB- and p38 kinase-dependent cyclooxygenase 2/prostaglandin E2 pathway
- PMID: 21551240
- PMCID: PMC3136338
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.10-178095
Intraplantar-injected ceramide in rats induces hyperalgesia through an NF-κB- and p38 kinase-dependent cyclooxygenase 2/prostaglandin E2 pathway
Abstract
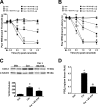
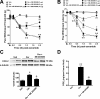
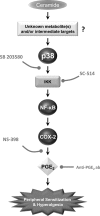
Inflammatory pain represents an important unmet clinical need with important socioeconomic implications. Ceramide, a potent proinflammatory sphingolipid, has been shown to elicit mechanical hyperalgesia, but the mechanisms remain largely unknown. We now demonstrate that, in addition to mechanical hyperalgesia, intraplantar injection of ceramide (10 μg) led to the development of thermal hyperalgesia that was dependent on induction of the inducible cyclooxygenase (COX-2) and subsequent increase of prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)). The development of mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia and increased production of PGE(2) was blocked by NS-398 (15-150 ng), a selective COX-2 inhibitor. The importance of the COX-2 to PGE(2) pathway in ceramide signaling was underscored by the findings that intraplantar injection of a monoclonal PGE(2) antibody (4 μg) blocked the development of hyperalgesia. Our results further revealed that COX-2 induction is regulated by NF-κB and p38 kinase activation, since intraplantar injection of SC-514 (0.1-1 μg) or SB 203580 (1-10 μg), well-characterized inhibitors of NF-κB and p38 kinase activation, respectively, blocked COX-2 induction and increased formation of PGE(2) and thermal hyperalgesia in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, activation of NF-κB was dependent on upstream activation of p38 MAPK, since SB 203580 (10 μg) blocked p65 phosphorylation, whereas p38 kinase phosphorylation was unaffected by NF-κB inhibition by SC-514 (1 μg). Our findings not only provide mechanistic insight into the signaling pathways engaged by ceramide in the development of hyperalgesia, but also provide a potential pharmacological basis for developing inhibitors targeting the ceramide metabolic-to-COX-2 pathway as novel analgesics.
Figures
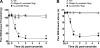
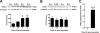

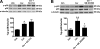
References
-
- Hannun Y. A., Obeid L. M. (2008) Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 9, 139–150 - PubMed
-
- Delgado A., Casas J., Llebaria A., Abad J. L., Fabrias G. (2006) Inhibitors of sphingolipid metabolism enzymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1758, 1957–1977 - PubMed
-
- Joseph E. K., Levine J. D. (2004) Caspase signalling in neuropathic and inflammatory pain in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 20, 2896–2902 - PubMed
-
- Vane J. R. (1971) Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat. New Biol. 231, 232–235 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

