Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate-induced contraction is increased in renal but not pulmonary arteries from DOCA-salt hypertensive rats
- PMID: 21551273
- PMCID: PMC3154666
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00084.2011
Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate-induced contraction is increased in renal but not pulmonary arteries from DOCA-salt hypertensive rats
Abstract
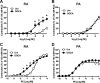
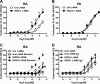
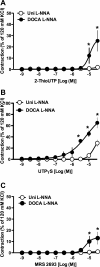
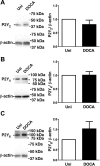
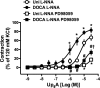
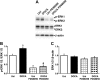
Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate (Up(4)A) was reported as a novel endothelium-derived contracting factor. Up(4)A contains both purine and pyrimidine moieties, which activate purinergic (P2)X and P2Y receptors. However, alterations in the vasoconstrictor responses to Up(4)A in hypertensive states remain unclear. The present study examined the effects of Up(4)A on contraction of isolated renal arteries (RA) and pulmonary arteries (PA) from DOCA-salt rats using isometric tension recording. RA from DOCA-salt rats exhibited increased contraction to Up(4)A versus arteries from control uninephrectomized rats in the absence and presence of N(G)-nitro-l-arginine (nitric oxide synthase inhibitor). On the other hand, the Up(4)A-induced contraction in PA was similar between the two groups. Up(4)A-induced contraction was inhibited by suramin (nonselective P2 antagonist) but not by diinosine pentaphosphate pentasodium salt hydrate (Ip(5)I; P2X(1) antagonist) in RA from both groups. Furthermore, 2-thiouridine 5'-triphosphate tetrasodium salt (2-ThioUTP; P2Y(2) agonist)-, uridine-5'-(γ-thio)-triphosphate trisodium salt (UTPγS; P2Y(2)/P2Y(4) agonist)-, and 5-iodouridine-5'-O-diphosphate trisodium salt (MRS 2693; P2Y(6) agonist)-induced contractions were all increased in RA from DOCA-salt rats. Protein expression of P2Y(2)-, P2Y(4)-, and P2Y(6) receptors in RA was similar between the two groups. In DOCA-salt RA, the enhanced Up(4)A-induced contraction was reduced by PD98059, an ERK pathway inhibitor, and Up(4)A-stimulated ERK activation was increased. These data are the first to indicate that Up(4)A-induced contraction is enhanced in RA from DOCA-salt rats. Enhanced P2Y receptor signaling and activation of the ERK pathway together represent a likely mechanism mediating the enhanced Up(4)A-induced contraction. Up(4)A might be of relevance in the pathophysiology of vascular tone regulation and renal dysfunction in arterial hypertension.
Figures
References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Boeynaems JM, Barnard EA, Boyer JL, Kennedy C, Knight GE, Fumagalli M, Gachet C, Jacobson KA, Weisman GA. International union of pharmacology LVIII: update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol Rev 58: 281–341, 2006 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bar I, Guns PJ, Metallo J, Cammarata D, Wilkin F, Boeynams JM, Bult H, Robaye B. Knockout mice reveal a role for P2Y6 receptor in macrophages, endothelial cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol 74: 777–784, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ, Liu SF. Regulation of pulmonary vascular tone. Pharmacol Rev 47: 87–131, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Benter IF, Canatan H, Benboubetra M, Yousif MH, Akhtar S. Global upregulation of gene expression associated with renal dysfunction in DOCA-salt-induced hypertensive rats occurs via signaling cascades involving epidermal growth factor receptor: a microarray analysis. Vascul Pharmacol 51: 101–109, 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

