Aim2 deficiency in mice suppresses the expression of the inhibitory Fcgamma receptor (FcgammaRIIB) through the induction of the IFN-inducible p202, a lupus susceptibility protein
- PMID: 21551362
- PMCID: PMC3110550
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003638
Aim2 deficiency in mice suppresses the expression of the inhibitory Fcgamma receptor (FcgammaRIIB) through the induction of the IFN-inducible p202, a lupus susceptibility protein
Abstract
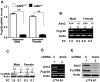
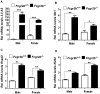
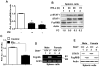
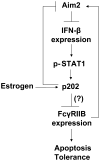
Murine Aim2 and Ifi202 genes (encoding for the Aim2 and p202 proteins) are members of the IFN-inducible Ifi200 gene family. The Aim2 deficiency in mice activates IFN signaling and stimulates the expression of the lupus susceptibility gene, the Ifi202, located within the NZB autoimmunity 2 (Nba2) interval. Given that the deficiency in the expression of the Fcgr2b gene (encoding for the inhibitory FcγRIIB receptor) is associated with increased lupus susceptibility in mice, we investigated whether the Aim2 protein could regulate the expression of Fcgr2b gene. In this article, we report that Aim2 deficiency in mice suppresses the expression of the FcγRIIB receptor. Interestingly, the Fcgr2b-deficient cells expressed increased levels of the IFN-β, activated IFN signaling, and expressed reduced levels of the Aim2 protein. Treatment of splenic cells with IFN-α or -γ reduced levels of the FcγRIIB mRNA and protein and also decreased the activity of the FcγRIIB p(-729/+585) Luc reporter. Moreover, levels of the FcγRIIB receptor were significantly higher in the Stat1-deficient splenic cells than in the wild-type cells. Accordingly, increased expression of IFN-β in lupus-prone B6.Nba2-ABC mice, as compared with non-lupus-prone C57BL/6 (B6) or B6.Nba2-C mice, was associated with reduced expression of the FcγRIIB receptor. Notably, overexpression of the p202 protein in cells decreased the expression of the Aim2 gene, activated the IFN response, and suppressed the expression of the Fcgr2b gene. These observations demonstrate that the expression of Aim2 protein is required to maintain the expression of the Fcgr2b gene and also predict epistatic interactions between the Ifi200 genes and the Fcgr2b gene within the Nba2 interval.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


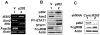
References
-
- Graham RR, Hom G, Ortmann W, Behrens TW. Review of recent genome-wide association scans in lupus. J Intern Med. 2009;265:680–688. - PubMed
-
- Kono DH, Theofilopoulos AN. Genetics of SLE in mice. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2006;28:83–96. - PubMed
-
- Morel L. Genetics of SLE: evidence from mouse models. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6:348–357. - PubMed
-
- Cohen-Solal JF, Jeganathan V, Grimaldi CM, Peeva E, Diamond B. Sex hormones and SLE: influencing the fate of autoreactive B cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;305:67–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

