Structure of C3PO and mechanism of human RISC activation
- PMID: 21552258
- PMCID: PMC3109212
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2032
Structure of C3PO and mechanism of human RISC activation
Abstract
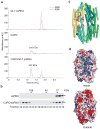
Assembly of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) consists of loading duplex (guide-passenger) siRNA onto Argonaute (Ago2) and removing the passenger strand. Ago2 contributes critically to RISC activation by nicking the passenger strand. Here we reconstituted duplex siRNA-initiated RISC activity using recombinant human Ago2 (hAgo2) and C3PO, indicating that C3PO has a critical role in hAgo2-RISC activation. Consistently, genetic depletion of C3PO compromised RNA silencing in mammalian cells. We determined the crystal structure of hC3PO, which reveals an asymmetric octamer barrel consisting of six translin and two TRAX subunits. This asymmetric assembly is critical for the function of C3PO as an endonuclease that cleaves RNA at the interior surface. The current work supports a Dicer-independent mechanism for human RISC activation, in which Ago2 directly binds duplex siRNA and nicks the passenger strand, and then C3PO activates RISC by degrading the Ago2-nicked passenger strand.
Figures

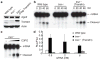

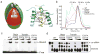


References
-
- Siomi H, Siomi MC. On the road to reading the RNA-interference code. Nature. 2009;457:396–404. - PubMed
-
- Liu Q, Paroo Z. Biochemical principles of small RNA pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79:295–319. - PubMed
-
- Kawamata T, Tomari Y. Trends Biochem Sci. Making RISC. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, et al. Argonaute2 is the catalytic engine of mammalian RNAi. Science. 2004;305:1437–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

