miR-135a contributes to paclitaxel resistance in tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 21552288
- PMCID: PMC3572709
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.148
miR-135a contributes to paclitaxel resistance in tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
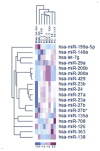
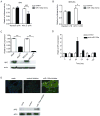
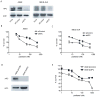
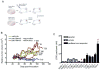
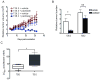
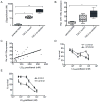
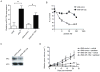
Cancer cell resistance to paclitaxel continues to be a major clinical problem. In this study, we utilized microRNA (miRNA) arrays to screen for differentially expressed miRNAs in paclitaxel-resistant cell lines established in vitro. We observed concordant upregulation of miR-135a in paclitaxel-resistant cell lines representing three human malignancies. Subsequently, the role of miRNA-135a was evaluated in an in vivo model of paclitaxel resistance. In this model, mice were inoculated subcutaneously with a non-small cell lung carcinoma cell line and treated with paclitaxel for a prolonged period. In paclitaxel-resistant cell lines, established either in vitro or in vivo, blockage of miR-135a sensitized resistant cell lines to paclitaxel-induced cell death. We further demonstrated a correlation between paclitaxel response and miR-135a expression in paclitaxel-resistant subclones that were established in vivo. The paclitaxel-resistant phenotype of these subclones was maintained upon retransplantation in new mice, as shown by decreased tumor response upon paclitaxel treatment compared with controls. Upregulation of miR-135a was associated with reduced expression of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene (APC). APC knockdown increased paclitaxel resistance in parental cell lines. Our results indicate that paclitaxel resistance is associated with upregulation of miR-135a, both in vitro and in vivo, and is in part determined by miR-135a-mediated downregulation of APC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
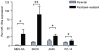
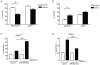
References
-
- Anand S, Penrhyn-Lowe S, Venkitaraman AR. AURORA-A amplification overrides the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint, inducing resistance to Taxol. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:51–62. - PubMed
-
- Aoki K, Taketo MM. Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC): a multi-functional tumor suppressor gene. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:3327–35. - PubMed
-
- Blower PE, Verducci JS, Lin S, Zhou J, Chung JH, Dai Z, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles for the NCI-60 cancer cell panel. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:1483–91. - PubMed
-
- Chu Q, Vincent M, Logan D, Mackay JA, Evans WK. Taxanes as first-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and practice guideline. Lung Cancer. 2005;50:355–74. - PubMed
-
- Cleveland WS. Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatter plots. J Amer Statist Assoc. 1979;74:829–836.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

