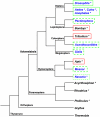
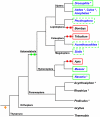
The phylogenetic origin of oskar coincided with the origin of maternally provisioned germ plasm and pole cells at the base of the Holometabola
- PMID: 21552321
- PMCID: PMC3084197
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002029
The phylogenetic origin of oskar coincided with the origin of maternally provisioned germ plasm and pole cells at the base of the Holometabola
Abstract
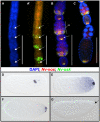
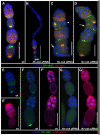
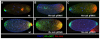
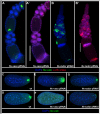
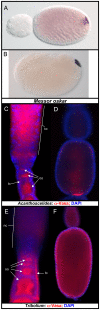
The establishment of the germline is a critical, yet surprisingly evolutionarily labile, event in the development of sexually reproducing animals. In the fly Drosophila, germ cells acquire their fate early during development through the inheritance of the germ plasm, a specialized maternal cytoplasm localized at the posterior pole of the oocyte. The gene oskar (osk) is both necessary and sufficient for assembling this substance. Both maternal germ plasm and oskar are evolutionary novelties within the insects, as the germline is specified by zygotic induction in basally branching insects, and osk has until now only been detected in dipterans. In order to understand the origin of these evolutionary novelties, we used comparative genomics, parental RNAi, and gene expression analyses in multiple insect species. We have found that the origin of osk and its role in specifying the germline coincided with the innovation of maternal germ plasm and pole cells at the base of the holometabolous insects and that losses of osk are correlated with changes in germline determination strategies within the Holometabola. Our results indicate that the invention of the novel gene osk was a key innovation that allowed the transition from the ancestral late zygotic mode of germline induction to a maternally controlled establishment of the germline found in many holometabolous insect species. We propose that the ancestral role of osk was to connect an upstream network ancestrally involved in mRNA localization and translational control to a downstream regulatory network ancestrally involved in executing the germ cell program.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Comment in
-
Long-lost relative claims orphan gene: oskar in a wasp.PLoS Genet. 2011 Apr;7(4):e1002045. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002045. Epub 2011 Apr 28. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21552332 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Extavour CG, Akam M. Mechanisms of germ cell specification across the metazoans: epigenesis and preformation. Development. 2003;130:5869–5884. - PubMed
-
- Extavour CGM. Evolution of the bilaterian germ line: lineage origin and modulation of specification mechanisms. Integrative and Comparative Biology. 2007;47:770–785. - PubMed
-
- Schwalm F. Insect Morphogenesis; In: Sauer HW, editor. Basel: Karger; 1988. - PubMed
-
- Hegner RW. Studies on germ cells. I. The history of the germ cells in insects with special reference to the Keimbahn-determinants. II. The origin and significance of the Keimbahn-determinants in animals. Journal of Morphology. 1914;25:375–509.
-
- Mahowald AP. Assembly of the Drosophila germ plasm. International Review of Cytology - a Survey of Cell Biology. 2001;Vol 203 203:187–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

