Beyond missing heritability: prediction of complex traits
- PMID: 21552331
- PMCID: PMC3084207
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002051
Beyond missing heritability: prediction of complex traits
Abstract
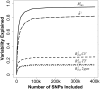
Despite rapid advances in genomic technology, our ability to account for phenotypic variation using genetic information remains limited for many traits. This has unfortunately resulted in limited application of genetic data towards preventive and personalized medicine, one of the primary impetuses of genome-wide association studies. Recently, a large proportion of the "missing heritability" for human height was statistically explained by modeling thousands of single nucleotide polymorphisms concurrently. However, it is currently unclear how gains in explained genetic variance will translate to the prediction of yet-to-be observed phenotypes. Using data from the Framingham Heart Study, we explore the genomic prediction of human height in training and validation samples while varying the statistical approach used, the number of SNPs included in the model, the validation scheme, and the number of subjects used to train the model. In our training datasets, we are able to explain a large proportion of the variation in height (h(2) up to 0.83, R(2) up to 0.96). However, the proportion of variance accounted for in validation samples is much smaller (ranging from 0.15 to 0.36 depending on the degree of familial information used in the training dataset). While such R(2) values vastly exceed what has been previously reported using a reduced number of pre-selected markers (<0.10), given the heritability of the trait (∼ 0.80), substantial room for improvement remains.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Huebinger RM, Garner HR, Barber RC. Pathway genetic load allows simultaneous evaluation of multiple genetic associations. Burns. 2010;36:787–792. - PubMed
-
- Visscher PM, Medland SE, Ferreira MAR, Morley KI, Zhu G, et al. Assumption-free estimation of heritability from genome-wide identity-by-descent sharing between full siblings. PLoS Genet. 2006;2:e41. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020041. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

