Using Blur to Affect Perceived Distance and Size
- PMID: 21552429
- PMCID: PMC3088122
- DOI: 10.1145/1731047.1731057
Using Blur to Affect Perceived Distance and Size
Abstract
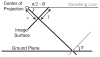
We present a probabilistic model of how viewers may use defocus blur in conjunction with other pictorial cues to estimate the absolute distances to objects in a scene. Our model explains how the pattern of blur in an image together with relative depth cues indicates the apparent scale of the image's contents. From the model, we develop a semiautomated algorithm that applies blur to a sharply rendered image and thereby changes the apparent distance and scale of the scene's contents. To examine the correspondence between the model/algorithm and actual viewer experience, we conducted an experiment with human viewers and compared their estimates of absolute distance to the model's predictions. We did this for images with geometrically correct blur due to defocus and for images with commonly used approximations to the correct blur. The agreement between the experimental data and model predictions was excellent. The model predicts that some approximations should work well and that others should not. Human viewers responded to the various types of blur in much the way the model predicts. The model and algorithm allow one to manipulate blur precisely and to achieve the desired perceived scale efficiently.
Figures


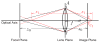
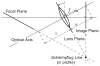
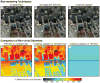
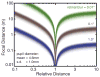




References
-
- Akeley K, Watt SJ, Girshick AR, Banks MS. A stereo display prototype with multiple focal distances. ACM Trans Graph. 2004;23(3):804–813.
-
- Barsky BA. Vision-Realistic rendering: Simulation of the scanned foveal image from wavefront data of human subjects. Proceedings of the 1st Symposium on Applied Perception in Graphics and Visualization (APGV’04); 2004. pp. 73–81.
-
- Barsky BA, Horn DR, Klein SA, Pang JA, Yu M. Camera models and optical systems used in computer graphics: Part I, Object-Based techniques. Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science and its Applications (ICCSA’03), Montreal, 2nd International Workshop on Computer Graphics and Geometric Modeling (CGGM’03); 2003a. pp. 246–255.
-
- Barsky BA, Horn DR, Klein SA, Pang JA, Yu M. Camera models and optical systems used in computer graphics: Part II, Image-Based techniques. Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science and its Applications (ICCSA’03), 2nd International Workshop on Computer Graphics and Geometric Modeling (CGGM’03); 2003b. pp. 256–265.
-
- Bell JA. Theory of mechanical miniatures in cinematography. Trans SMPTE. 1924;18:119.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
