A new crystal form of mouse thiamin pyrophosphokinase
- PMID: 21552434
- PMCID: PMC3088427
A new crystal form of mouse thiamin pyrophosphokinase
Abstract
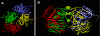
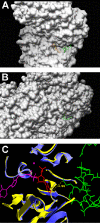
Thiamin pyrophosphokinase (TPK) transfers a pyrophosphate group from ATP to the hydroxyl group of thiamin and produces thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP). TPP is the cofactor of metabolically important enzymes such as pyruvate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase, transketolase and 2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA lyase. Thiamin deficiency results in Wernike-Korsakof Syndrome (WKS) due to neurological disorder and wet beriberi, a potentially fatal cardiovascular disease. Mouse TPK associates as a dimer revealed by previous solved crystallographic structures. In this study, we report mouse TPK complexed with TPP-Mg(2+) and thiamin -Mg(2+), respectively, in a new crystal form. In these two structures, four mouse TPK molecules were found in each asymmetric unit. Although we cannot rule out this tetramer form can be an artifact from crystal packing, mouse TPK tetramer has a more closed ATP binding pocket and has the potential to provide specific interactions between mouse TPK and ATP compared with the previous dimeric structure and is likely to be an active form.
Keywords: TPP-Mg2+; Thiamin pyrophosphokinase (TPK); crystal structure; dimer; protein oligomerization; tetramer; thiamin-Mg2+.
Figures

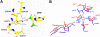
References
-
- Ishii K, Sarai K, Sanemori H, Kawasaki T. Concentrations of thiamine and its phosphate esters in rat tissues determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Nutr SciVitaminol (Tokyo) 1979;25:517–523. - PubMed
-
- Kimura M, Itokawa Y. Determination of thiamin and thiamin phosphate esters in blood by liquid chromatography with post-column derivatization. Clin Chem. 1983;29:2073–2075. - PubMed
-
- Bettendorff L, Peeters M, Wins P, Schoffeniels E. Metabolism of thiamine triphosphate in rat brain: correlation with chloride permeability. J Neurochem. 1993;60:423–434. - PubMed
-
- Shikata H, Egi Y, Koyama S, Yamada K, Kawasaki T. Properties of the thiamin triphosphate-synthesizing activity catalyzed by adenylate kinase (isoenzyme 1) Biochem Int. 1989;18:943–949. - PubMed
-
- Nosaka K, Kaneko Y, Nishimura H, Iwa-shima A. A possible role for acid phosphatase with thiamin-binding activity encoded by PH03 in yeast. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989;51:55–59. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
