Biochemistry of eukaryotic homologous recombination
- PMID: 21552479
- PMCID: PMC3087616
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-71021-9
Biochemistry of eukaryotic homologous recombination
Abstract
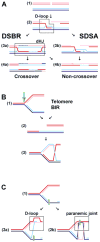
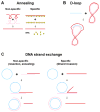
The biochemistry of eukaryotic homologous recombination caught fire with the discovery that Rad51 is the eukaryotic homolog of the bacterial RecA and T4 UvsX proteins; and this field is still hot. The core reaction of homologous recombination, homology search and DNA strand invasion, along with the proteins catalyzing it, are conserved throughout evolution in principle. However, the increased complexity of eukaryotic genomes and the diversity of eukaryotic cell biology pose additional challenges to the recombination machinery. It is not surprising that this increase in complexity coincided with the evolution of new recombination proteins and novel support pathways, as well as changes in the properties of those eukaryotic recombination proteins that are evidently conserved in evolution. In humans, defects in homologous recombination lead to increased cancer predisposition, underlining the importance of this pathway for genomic stability and tumor suppression. This review will focus on the mechanisms of homologous recombination in eukaryotes as elucidated by the biochemical analysis of yeast and human proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Aihara H, Ito Y, Kurumizaka H, Yokoyama S, Shibata T. The N-terminal domain of the human Rad51 protein binds DNA: Structure and a DNA binding surface as revealed by NMR. J Mol Biol. 1999;290:495–504. - PubMed
-
- Alexeev A, Mazin A, Kowalczykowski SC. Rad54 protein possesses chromatin-remodeling activity stimulated by a Rad51-ssDNA nucleoprotein filament. Nature Struct Biol. 2003;10:182–186. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
