The complete genome sequence of 'Candidatus Liberibacter solanacearum', the bacterium associated with potato zebra chip disease
- PMID: 21552483
- PMCID: PMC3084294
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019135
The complete genome sequence of 'Candidatus Liberibacter solanacearum', the bacterium associated with potato zebra chip disease
Abstract
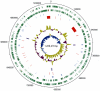
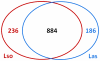
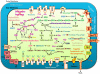
Zebra Chip (ZC) is an emerging plant disease that causes aboveground decline of potato shoots and generally results in unusable tubers. This disease has led to multi-million dollar losses for growers in the central and western United States over the past decade and impacts the livelihood of potato farmers in Mexico and New Zealand. ZC is associated with 'Candidatus Liberibacter solanacearum', a fastidious alpha-proteobacterium that is transmitted by a phloem-feeding psyllid vector, Bactericera cockerelli Sulc. Research on this disease has been hampered by a lack of robust culture methods and paucity of genome sequence information for 'Ca. L. solanacearum'. Here we present the sequence of the 1.26 Mbp metagenome of 'Ca. L. solanacearum', based on DNA isolated from potato psyllids. The coding inventory of the 'Ca. L. solanacearum' genome was analyzed and compared to related Rhizobiaceae to better understand 'Ca. L. solanacearum' physiology and identify potential targets to develop improved treatment strategies. This analysis revealed a number of unique transporters and pathways, all potentially contributing to ZC pathogenesis. Some of these factors may have been acquired through horizontal gene transfer. Taxonomically, 'Ca. L. solanacearum' is related to 'Ca. L. asiaticus', a suspected causative agent of citrus huanglongbing, yet many genome rearrangements and several gene gains/losses are evident when comparing these two Liberibacter. species. Relative to 'Ca. L. asiaticus', 'Ca. L. solanacearum' probably has reduced capacity for nucleic acid modification, increased amino acid and vitamin biosynthesis functionalities, and gained a high-affinity iron transport system characteristic of several pathogenic microbes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


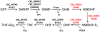
References
-
- Gudmestad NC, Secor GA. Zebra Chip: A new disease of potato. Nebr Potato Eyes. 2007;19:1–4.
-
- Secor GA, Rivera VV, Abad JA, Lee I-M, Clover GRG, et al. Association of ‘Candidatus Liberibacter solanacearum’ with zebra chip disease of potato established by graft and psyllid transmission, electron microscopy, and PCR. Plant Dis. 2009;93:574–583. - PubMed
-
- Munyaneza JE, Fisher TW, Sengoda VG, Garczynski SF, Nissinen A, et al. Association of ‘Candidatus Liberibacter solanacearum’ with the psyllid, Trioza apicalis (Hemiptera: Triozidae) in Europe. J of Economic Entomol. 2010;103:1060–1070. - PubMed
-
- Lin H, Doddapaneni H, Munyaneza JE, Civerolo EL, Sengoda VG, et al. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA from a new ‘Candidatus Liberibacter’ strain associated with zebra chip disease of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) and the potato psyllid (Bactericera cockerelli sulc). J of Plant Pathol. 2009;91:215–219.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

