Antibody engineering using phage display with a coiled-coil heterodimeric Fv antibody fragment
- PMID: 21552519
- PMCID: PMC3084267
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019023
Antibody engineering using phage display with a coiled-coil heterodimeric Fv antibody fragment
Abstract
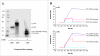
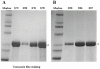
A Fab-like antibody binding unit, ccFv, in which a pair of heterodimeric coiled-coil domains was fused to V(H) and V(L) for Fv stabilization, was constructed for an anti-VEGF antibody. The anti-VEGF ccFv showed the same binding affinity as scFv but significantly improved stability and phage display level. Furthermore, phage display libraries in the ccFv format were constructed for humanization and affinity maturation of the anti-VEGF antibody. A panel of V(H) frameworks and V(H)-CDR3 variants, with a significant improvement in affinity and expressibility in both E. coli and yeast systems, was isolated from the ccFv phage libraries. These results demonstrate the potential application of the ccFv antibody format in antibody engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kontermann RE. Alternative antibody formats. Curr Opin Mol Ther . 2010;12:176–183. - PubMed
-
- Bird RE, Hardman KD, Jacobson JW, Johnson S, Kaufman BM, et al. Single-chain antigen-binding proteins. Science. 1988;242:423–426. - PubMed
-
- Kortt AA, Malby RL, Caldwell JB, Gruen LC, Ivancic N, et al. Recombinant anti-sialidase single-chain variable fragment antibody. Eur J Biochem . 1994;221:151–157. Characterization, formation ofdimer and higher-molecular-mass multimers and the solution of the crystal structure of the single-chain variable fragment/sialidase complex. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

