GPVI and GPIbα mediate staphylococcal superantigen-like protein 5 (SSL5) induced platelet activation and direct toward glycans as potential inhibitors
- PMID: 21552524
- PMCID: PMC3084272
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019190
GPVI and GPIbα mediate staphylococcal superantigen-like protein 5 (SSL5) induced platelet activation and direct toward glycans as potential inhibitors
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a common pathogen capable of causing life-threatening infections. Staphylococcal superantigen-like protein 5 (SSL5) has recently been shown to bind to platelet glycoproteins and induce platelet activation. This study investigates further the interaction between SSL5 and platelet glycoproteins. Moreover, using a glycan discovery approach, we aim to identify potential glycans to therapeutically target this interaction and prevent SSL5-induced effects.
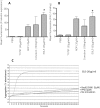
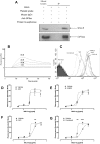
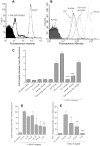
Methodology/principal findings: In addition to platelet activation experiments, flow cytometry, immunoprecipitation, surface plasmon resonance and a glycan binding array, were used to identify specific SSL5 binding regions and mediators. We independently confirm SSL5 to interact with platelets via GPIbα and identify the sulphated-tyrosine residues as an important region for SSL5 binding. We also identify the novel direct interaction between SSL5 and the platelet collagen receptor GPVI. Together, these receptors offer one mechanistic explanation for the unique functional influences SSL5 exerts on platelets. A role for specific families of platelet glycans in mediating SSL5-platelet interactions was also discovered and used to identify and demonstrate effectiveness of potential glycan based inhibitors in vitro.
Conclusions/significance: These findings further elucidate the functional interactions between SSL5 and platelets, including the novel finding of a role for the GPVI receptor. We demonstrate efficacy of possible glycan-based approaches to inhibit the SSL5-induced platelet activation. Our data warrant further work to prove SSL5-platelet effects in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Staphylococcal superantigen-like 5 activates platelets and supports platelet adhesion under flow conditions, which involves glycoprotein Ibalpha and alpha IIb beta 3.J Thromb Haemost. 2009 Nov;7(11):1867-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03564.x. Epub 2009 Jul 28. J Thromb Haemost. 2009. PMID: 19656281
-
Role of sialic acid-containing glycans of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in the interaction between MMP-9 and staphylococcal superantigen-like protein 5.Microbiol Immunol. 2018 Mar;62(3):168-175. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12573. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Microbiol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29328525
-
GPIbalpha-selective activation of platelets induces platelet signaling events comparable to GPVI activation events.Platelets. 2010;21(4):244-52. doi: 10.3109/09537101003695339. Platelets. 2010. PMID: 20367574
-
Structure-activity relationships of snake toxins targeting platelet receptors, glycoprotein Ib-IX-V and glycoprotein VI.Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2003 Jun;1(2):143-9. doi: 10.2174/1568016033477559. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2003. PMID: 15320694 Review.
-
Platelets and primary haemostasis.Thromb Res. 2012 Mar;129(3):220-4. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2011.11.036. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Thromb Res. 2012. PMID: 22178577 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of homocysteine on regulating immunothrombosis: mechanisms and therapeutic potential in management of infections.Inflamm Res. 2025 May 24;74(1):86. doi: 10.1007/s00011-025-02045-0. Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40413366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Superantigens and SARS-CoV-2.Pathogens. 2022 Mar 23;11(4):390. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11040390. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35456065 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the Complex Relationships Between the Hemostasis System and Infective Endocarditis.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 4;14(11):3965. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113965. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcal manipulation of host immune responses.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015 Sep;13(9):529-43. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3521. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26272408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Era of Thromboinflammation: Platelets Are Dynamic Sensors and Effector Cells During Infectious Diseases.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 13;10:2204. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02204. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31572400 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Petti CA, Fowler VG., Jr Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and endocarditis. Cardiol Clin. 2003;21:219–233, vii. - PubMed
-
- Moreillon P, Que YA. Infective endocarditis. Lancet. 2004;363:139–149. - PubMed
-
- Kessler CM, Tang Z, Jacobs HM, Szymanski LM. The suprapharmacologic dosing of antithrombin concentrate for Staphylococcus aureus-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation in guinea pigs: substantial reduction in mortality and morbidity. Blood. 1997;89:4393–4401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

