The phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor vardenafil is a potent inhibitor of ABCB1/P-glycoprotein transporter
- PMID: 21552528
- PMCID: PMC3084276
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019329
The phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor vardenafil is a potent inhibitor of ABCB1/P-glycoprotein transporter
Abstract
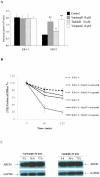
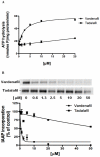
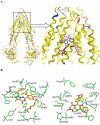
One of the major causes of chemotherapy failure in cancer treatment is multidrug resistance (MDR) which is mediated by the ABCB1/P-glycoprotein. Previously, through the use of an extensive screening process, we found that vardenafil, a phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE-5) inhibitor significantly reverses MDR in ABCB1 overexpressing cancer cells, and its efficacy was greater than that of tadalafil, another PDE-5 inhibitor. The present study was designed to determine the reversal mechanisms of vardenafil and tadalafil on ABC transporters-mediated MDR. Vardenafil or tadalafil alone, at concentrations up to 20 µM, had no significant toxic effects on any of the cell lines used in this study, regardless of their membrane transporter status. However, vardenafil when used in combination with anticancer substrates of ABCB1, significantly potentiated their cytotoxicity in ABCB1 overexpressing cells in a concentration-dependent manner, and this effect was greater than that of tadalafil. The sensitivity of the parenteral cell lines to cytotoxic anticancer drugs was not significantly altered by vardenafil. The differential effects of vardenafil and tadalafil appear to be specific for the ABCB1 transporter as both vardenafil and tadalafil had no significant effect on the reversal of drug resistance conferred by ABCC1 (MRP1) and ABCG2 (BCRP) transporters. Vardenafil significantly increased the intracellular accumulation of [(3)H]-paclitaxel in the ABCB1 overexpressing KB-C2 cells. In addition, vardenafil significantly stimulated the ATPase activity of ABCB1 and inhibited the photolabeling of ABCB1 with [(125)I]-IAAP. Furthermore, Western blot analysis indicated the incubation of cells with either vardenafil or tadalafil for 72 h did not alter ABCB1 protein expression. Overall, our results suggest that vardenafil reverses ABCB1-mediated MDR by directly blocking the drug efflux function of ABCB1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lapatinib (Tykerb, GW572016) reverses multidrug resistance in cancer cells by inhibiting the activity of ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 1 and G member 2.Cancer Res. 2008 Oct 1;68(19):7905-14. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0499. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18829547 Free PMC article.
-
PD173074, a selective FGFR inhibitor, reverses ABCB1-mediated drug resistance in cancer cells.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013 Jul;72(1):189-99. doi: 10.1007/s00280-013-2184-z. Epub 2013 May 15. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23673445 Free PMC article.
-
PDE5 inhibitors, sildenafil and vardenafil, reverse multidrug resistance by inhibiting the efflux function of multidrug resistance protein 7 (ATP-binding Cassette C10) transporter.Cancer Sci. 2012 Aug;103(8):1531-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02328.x. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Cancer Sci. 2012. PMID: 22578167 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors: molecular pharmacology and interactions with other phosphodiesterases.Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(31):4047-58. doi: 10.2174/138161205774913426. Curr Pharm Des. 2005. PMID: 16378510 Review.
-
Cardiovascular effects of the 3 phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors approved for the treatment of erectile dysfunction.Circulation. 2004 Nov 9;110(19):3149-55. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000146906.42375.D3. Circulation. 2004. PMID: 15533876 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A dual PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 reverses doxorubicin resistance in ABCB1 overexpressing ovarian and pancreatic cancer cell lines.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020 Jun;1864(6):129556. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129556. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020. PMID: 32061787 Free PMC article.
-
Motesanib (AMG706), a potent multikinase inhibitor, antagonizes multidrug resistance by inhibiting the efflux activity of the ABCB1.Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Aug 15;90(4):367-78. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2014.06.006. Epub 2014 Jun 14. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24937702 Free PMC article.
-
bba, a synthetic derivative of 23-hydroxybutulinic acid, reverses multidrug resistance by inhibiting the efflux activity of MRP7 (ABCC10).PLoS One. 2013 Sep 17;8(9):e74573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074573. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24069321 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances regarding the role of ABC subfamily C member 10 (ABCC10) in the efflux of antitumor drugs.Chin J Cancer. 2014 May;33(5):223-30. doi: 10.5732/cjc.013.10122. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Chin J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24103790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of 5-oxyquinoline derivatives for reversal of multidrug resistance.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2012;8:1700-4. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.8.193. Epub 2012 Oct 5. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2012. PMID: 23209502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deeley RG, Westlake C, Cole SP. Transmembrane transport of endo- and xenobiotics by mammalian ATP-binding cassette multidrug resistance proteins. Physiol Rev. 2006;86:849–899. - PubMed
-
- Shabbits JA, Krishna R, Mayer LD. Molecular and pharmacological strategies to overcome multidrug resistance. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2001;1:585–594. - PubMed
-
- Dean M, Rzhetsky A, Allikmets R. The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. Genome Res. 2001;11:1156–1166. - PubMed
-
- O'Connor R. The pharmacology of cancer resistance. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:1267–1272. - PubMed
-
- Glavinas H, Krajcsi P, Cserepes J, Sarkadi B. The role of ABC transporters in drug resistance, metabolism and toxicity. Curr Drug Deliv. 2004;1:27–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

