Structural basis for variant-specific neuroligin-binding by α-neurexin
- PMID: 21552542
- PMCID: PMC3084293
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019411
Structural basis for variant-specific neuroligin-binding by α-neurexin
Abstract
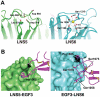
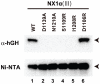
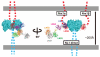
Neurexins (Nrxs) are presynaptic membrane proteins with a single membrane-spanning domain that mediate asymmetric trans-synaptic cell adhesion by binding to their postsynaptic receptor neuroligins. α-Nrx has a large extracellular region comprised of multiple copies of laminin, neurexin, sex-hormone-binding globulin (LNS) domains and epidermal growth factor (EGF) modules, while that of β-Nrx has but a single LNS domain. It has long been known that the larger α-Nrx and the shorter β-Nrx show distinct binding behaviors toward different isoforms/variants of neuroligins, although the underlying mechanism has yet to be elucidated. Here, we describe the crystal structure of a fragment corresponding to the C-terminal one-third of the Nrx1α ectodomain, consisting of LNS5-EGF3-LNS6. The 2.3 Å-resolution structure revealed the presence of a domain configuration that was rigidified by inter-domain contacts, as opposed to the more common flexible "beads-on-a-string" arrangement. Although the neuroligin-binding site on the LNS6 domain was completely exposed, the location of the α-Nrx specific LNS5-EGF3 segment proved incompatible with the loop segment inserted in the B+ neuroligin variant, which explains the variant-specific neuroligin recognition capability observed in α-Nrx. This, combined with a low-resolution molecular envelope obtained by a single particle reconstruction performed on negatively stained full-length Nrx1α sample, allowed us to derive a structural model of the α-Nrx ectodomain. This model will help us understand not only how the large α-Nrx ectodomain is accommodated in the synaptic cleft, but also how the trans-synaptic adhesion mediated by α- and β-Nrxs could differentially affect synaptic structure and function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
A splice code for trans-synaptic cell adhesion mediated by binding of neuroligin 1 to alpha- and beta-neurexins.Neuron. 2005 Oct 20;48(2):229-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.08.026. Neuron. 2005. PMID: 16242404
-
Splice form dependence of beta-neurexin/neuroligin binding interactions.Neuron. 2010 Jul 15;67(1):61-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.06.001. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20624592 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Trans-Synaptic Neurexin-Neuroligin Interaction in Pathological Pain.Cells. 2022 Jun 16;11(12):1940. doi: 10.3390/cells11121940. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35741069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The structure of neurexin 1α reveals features promoting a role as synaptic organizer.Structure. 2011 Jun 8;19(6):779-89. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2011.03.012. Epub 2011 May 27. Structure. 2011. PMID: 21620716 Free PMC article.
-
Neurexin-neuroligin signaling in synapse development.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007 Feb;17(1):43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2007.01.011. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17275284 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structures of neurexophilin-neurexin complexes reveal a regulatory mechanism of alternative splicing.EMBO J. 2019 Nov 15;38(22):e101603. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019101603. Epub 2019 Sep 30. EMBO J. 2019. PMID: 31566781 Free PMC article.
-
Neurexins.Genome Biol. 2013;14(9):213. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-9-213. Genome Biol. 2013. PMID: 24083347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A matter of balance: role of neurexin and neuroligin at the synapse.Neurochem Res. 2013 Jun;38(6):1174-89. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1029-9. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23559421 Review.
-
Hot Spots for Protein Partnerships at the Surface of Cholinesterases and Related α/β Hydrolase Fold Proteins or Domains-A Structural Perspective.Molecules. 2017 Dec 23;23(1):35. doi: 10.3390/molecules23010035. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29295471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal and non-neuronal functions of the synaptic cell adhesion molecule neurexin in Nematostella vectensis.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 1;15(1):6495. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50818-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39090098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dean C, Dresbach T. Neuroligins and neurexins: linking cell adhesion, synapse formation and cognitive function. Trends Neurosci. 2006;29:21–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

