Breast ultrasound diagnostic performance and outcomes for mass lesions using Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System category 0 mammogram
- PMID: 21552670
- PMCID: PMC3072469
- DOI: 10.1590/s1807-59322011000300014
Breast ultrasound diagnostic performance and outcomes for mass lesions using Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System category 0 mammogram
Abstract
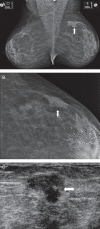
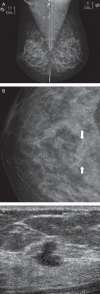
Purpose: To evaluate the outcomes and diagnostic performance of ultrasonography after a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (Bi-RADS) category 0 mammogram.
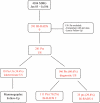
Material and methods: This retrospective study reviewed 4,384 consecutive patients who underwent a screening mammography from January 2005 to July 2006; 391 of the 4,384 exams were classified as Bi-RADS category 0. After exclusions, 241 patients received subsequent sonogram. Ultrasonography was considered diagnostic when the Bi-RADS category was changed to 2, 4, or 5, and it was considered indeterminate (Bi-RADS 3) when the results indicated that the patients should return for a mammographic follow-up. The outcomes of these patients were assessed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of ultrasonography.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 53.3 years (ranging from 35 to 81). Of the 241 patients, ultrasonography was considered diagnostic in 146 (60.6%) patients and indeterminate in 95 (39.4%) patients. In the diagnostic group, 111 out of 146 patients (70.2%) had a sonogram result of Bi-RADS category 2 after a 2-year follow-up without evidence of malignancy. Furthermore, 35 out of 146 patients (29.8%) had a suspicious sonogram with a result of Bi-RADS category 4. After a tissue sampling procedure, 10 patients were confirmed to have breast cancer, and 25 had benign histopathological features without any evidence of malignancy after a 2-year follow-up. The sensitivity of ultrasonography was 100%, specificity was 89.1%, and overall accuracy was 89.6%.
Conclusions: Based on the degree of resolution and its diagnostic performance, ultrasonography was determined to be an excellent method for the subsequent evaluation of Bi-RADS 0 mammograms.
Figures
References
-
- American College of Radiology (ACR) Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS™), 4rd edition. American College of Radiology, Reston, Va. 2003
-
- Mainiero M, Goldkamp A, Lazarus E, Livingston L, Koelliker SL, Schepps B, et al. Characterization of breast masses with sonography. Can biopsy of some solid masses be deferred. J Ultrasound Med. 2005;24:161–7. - PubMed
-
- Stavros AT, Thickman D, Rapp CL, Dennis MA, Parker SH, Sisney GA. Solid breast nodules: use of sonography to distinguish between benign and malignant lesions. Radiology. 1995;196:123–34. - PubMed
-
- Rahbar G, Sie AC, Hansen GC, Prince JS, Melany ML, Reynolds HE, et al. Benign versus malignant solid breast masses: US differentiation. Radiology. 1999;213:889–94. - PubMed
-
- Berg WA, Blume JD, Cormack JB, Mendelson EB, Lehrer D, Böhm-Vélez M, et al. Combined screening with ultrasound and mammography vs. mammography alone in women at elevated risk of breast cancer. JAMA. 2008;299:2151–63. 10.1001/jama.299.18.2151 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

