In vitro dentin permeability after application of Gluma® desensitizer as aqueous solution or aqueous fumed silica dispersion
- PMID: 21552716
- PMCID: PMC4243753
- DOI: 10.1590/s1678-77572011000200011
In vitro dentin permeability after application of Gluma® desensitizer as aqueous solution or aqueous fumed silica dispersion
Abstract
Objectives: To assess and to compare the effects of Gluma® Desensitizer (GDL) with an experimental glutaraldehyde and HEMA containing fumed silica dispersion (GDG) on dentin permeability using a chemiluminous tracer penetration test.
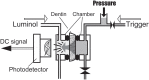
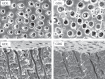
Material and methods: Twenty disc-shaped dentin specimens were dissected from extracted human third molars. The dentin specimens were mounted in a split chamber device for determination of permeability under liquid pressure using a photochemical method. Ten specimens were randomly selected and allocated to the evaluation groups Gluma® Desensitizer as aqueous solution and glutaraldehyde/HEMA as fumed silica dispersion, respectively. Dentin disc permeability was determined at two pressure levels after removal of smear with EDTA, after albumin soaking, and after application of the desensitizing agents. Two desensitizer-treated and rinsed specimens of each group were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) for surface remnants.
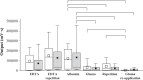
Results: Comparatively large standard deviations of the mean EDTA reference and albumin soaked samples permeability values reflected the differences of the dentin substrates. The mean chemiluminescence values of specimen treated with GDL and GDG, respectively, were significantly reduced after topical application of the desensitizing agents on albumin-soaked dentin. The effects of GDL and GDG on permeability were not significantly different. Treated specimens showed no surface remnants after rinsing.
Conclusions: The experimental desensitizer gel formulation reduced dentin permeability as effectively as the original Gluma® Desensitizer solution.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Occlusion, acid resistance, and elemental characterization of dentin treated with desensitizing agents.Braz Oral Res. 2025 Feb 7;39:e016. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2025.vol39.016. eCollection 2025. Braz Oral Res. 2025. PMID: 39936715 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of desensitizing agents on dentin permeability.Am J Dent. 2009 Jun;22(3):143-6. Am J Dent. 2009. PMID: 19650593
-
Effect of two desensitizing agents on dentin permeability in vitro.J Appl Oral Sci. 2017 Jan-Feb;25(1):34-41. doi: 10.1590/1678-77572016-0228. J Appl Oral Sci. 2017. PMID: 28198974 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dentin desensitizers and dentin bonding agents on dentin permeability.Am J Dent. 2000 Feb;13(1):21-7. Am J Dent. 2000. PMID: 11763898
-
Effectiveness and acid/tooth brushing resistance of in-office desensitizing treatments-A hydraulic conductance study.Arch Oral Biol. 2018 Dec;96:130-136. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Arch Oral Biol. 2018. PMID: 30237094
Cited by
-
Evaluation of different treatment protocols for dentin hypersensitivity: an 18-month randomized clinical trial.Lasers Med Sci. 2017 Jul;32(5):1023-1030. doi: 10.1007/s10103-017-2203-0. Epub 2017 Apr 8. Lasers Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28391435 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of Five Different Desensitizers: A Comparative Dentin Permeability and SEM Investigation In Vitro.Open Dent J. 2017 Jan 31;11:15-33. doi: 10.2174/1874210601711010015. eCollection 2017. Open Dent J. 2017. PMID: 28484578 Free PMC article.
-
Occlusion, acid resistance, and elemental characterization of dentin treated with desensitizing agents.Braz Oral Res. 2025 Feb 7;39:e016. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2025.vol39.016. eCollection 2025. Braz Oral Res. 2025. PMID: 39936715 Free PMC article.
-
Dentinal tubule occlusion using Er:YAG Laser: an in vitro study.J Appl Oral Sci. 2021 Apr 2;29:e20200266. doi: 10.1590/1678-7757-2020-0266. eCollection 2021. J Appl Oral Sci. 2021. PMID: 33825761 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of erosive and abrasive stress on sealing ability of different desensitizers: In-vitro study.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 1;14(8):e0220823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220823. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31369650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arrais CA, Chan DC, Giannini M. Effects of desensitizing agents on dentinal tubule occlusion. J Appl Oral Sci. 2004;12:144–148. - PubMed
-
- Bergenholtz G, Jontell M, Tuttle A, Knutsson G. Inhibition of serum albumin flux across exposed dentine following conditioning with GLUMA primer, glutaraldehyde or potassium oxalates. J Dent. 1993;21:220–227. - PubMed
-
- Brännström M. Sensitivity of dentine. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1966;21:517–526. - PubMed
-
- Brännström M, Lindén LA, Aström A. The hydrodynamics of the dental tubule and of pulp fluid. A discussion of its significance in relation to dentinal sensitivity. Caries Res. 1967;1:310–317. - PubMed
-
- Brännström M. The transmission and control of dentinal pain. In: Grossman LI, editor. Mechanism and control of pain. New York: Masson Pub. Co.; 1979. pp. 15–35.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

