Inhibition of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) reduces ventricular tachycardia risk by altering connexin43
- PMID: 21553032
- PMCID: PMC3156477
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-011-0761-3
Inhibition of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) reduces ventricular tachycardia risk by altering connexin43
Abstract
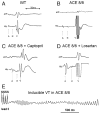
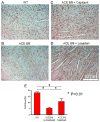
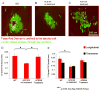
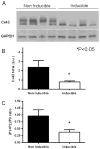
Renin-angiotensin system (RAS) activation is associated with arrhythmias. We investigated the effects of RAS inhibition in cardiac-specific angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) overexpression (ACE 8/8) mice, which exhibit proclivity to ventricular tachycardia (VT) and sudden death because of reduced connexin43 (Cx43). ACE 8/8 mice were treated with an ACE inhibitor (captopril) or an angiotensin receptor type-1 blocker (losartan). Subsequently, electrophysiological studies were performed, and the hearts were extracted for Cx43 quantification using immunoblotting, immunohistochemistry, fluorescent dye spread method, and sodium current quantification using whole cell patch clamping. VT was induced in 12.5% of captopril-treated ACE 8/8 and in 28.6% of losartan-treated mice compared to 87.5% of untreated mice (P < 0.01). Losartan and captopril treatment increased total Cx43 2.4-fold (P = 0.01) and the Cx43 phosphorylation ratio 2.3-fold (P = 0.005). Treatment was associated with a recovery of gap junctional conductance. Survival in treated mice improved to 0.78 at 10 weeks (95% confidence interval 0.64 to 0.92), compared to the expected survival of less than 0.50. In a model of RAS activation, arrhythmic risk was correlated with reduced Cx43 amount and phosphorylation. RAS inhibition resulted in increased total and phosphorylated Cx43, decreased VT inducibility, and improved survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
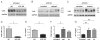
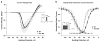
References
-
- Swedberg K, Kjekshus J. Effects of enalapril on mortality in severe congestive heart failure: results of the Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study (CONSENSUS) Am J Cardiol. 1988;62:60A–66A. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Sleight P, Pogue J, Bosch J, Davies R, Dagenais G. Effects of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients the heart outcomes prevention evaluation study investigators. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:145–153. - PubMed
-
- Pitt B, Zannad F, Remme WJ, Cody R, Castaigne A, Perez A, Palensky J, Wittes J. The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure randomized aldactone evaluation study investigators. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:709–717. - PubMed
-
- Pitt B, Remme W, Zannad F, Neaton J, Martinez F, Roniker B, Bittman R, Hurley S, Kleiman J, Gatlin M. Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1309–1321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

