Reinfection after two-stage revision for periprosthetic infection of total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 21553042
- PMCID: PMC3251662
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-011-1267-x
Reinfection after two-stage revision for periprosthetic infection of total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
Purpose: Limited data exist regarding the long-term results or risk factors for failure after two-stage reimplantation for periprosthetic knee infection. The purpose of this retrospective review was to investigate infection-free implant survival and identify variables associated with reinfection after this procedure. Furthermore, a staging system was evaluated as a possible prognostic tool for patients undergoing two-stage reimplantation of infected total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
Methods: In this level II, retrospective prognostic study, 368 patients with infected TKA treated with a two-stage revision protocol at our institution between 1998 and 2006 were reviewed. Patients who developed recurrent infection and an equal number of patients randomly selected for the control group were analysed for risk factors associated with treatment failure.
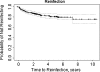
Results: At the most recent follow-up, 58 (15.8%) patients had developed reinfection after the two-stage reimplantation. The median time to reinfection was 1,303 days (3.6 years), with follow-up time ranging from six to 2,853 days (7.8 years). The strongest positive predictors of treatment failure included chronic lymphoedema [hazard ratio (HR) = 2.28, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.16-4.48; p = 0.02),and revision between resection and definitive reimplantation (HR = 2.13, 95% CI 1.20-3.79; p = 0.01, whereas patients treated with intravenously administered Cefazolin had a significant reduction in recurrent infection rate (HR = 0.48, 95% CI 0.25-0.90; p = 0.02).
Conclusions: Our findings should be of help in counselling patients regarding their prognosis when faced with two-stage exchange for infected TKA and provide a basis for future comparisons.
Figures
References
-
- Salgado CD, Dash S, Cantey JR, Marculescu CE. Higher risk of failure of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;461:48–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical