Clinical results of radionuclide therapy of neuroendocrine tumours with 90Y-DOTATATE and tandem 90Y/177Lu-DOTATATE: which is a better therapy option?
- PMID: 21553086
- PMCID: PMC3168754
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-011-1833-x
Clinical results of radionuclide therapy of neuroendocrine tumours with 90Y-DOTATATE and tandem 90Y/177Lu-DOTATATE: which is a better therapy option?
Abstract
Purpose: Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) using radiolabelled somatostatin analogues is a treatment option for patients with disseminated neuroendocrine tumours (NET). A combination treatment using the high-energy 90Y beta emitter for larger lesions and the lower energy 177Lu for smaller lesions has been postulated in the literature.The aim of the study was to evaluate combined 90Y/177Lu-DOTATATE therapy in comparison to 90Y-DOTATATE alone.
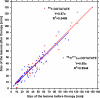
Methods: Fifty patients with disseminated NET were included in the study prospectively and divided into two groups: group A (n=25) was treated with 90Y-DOTATATE, whereas group B (n=25) received the 1:1 90Y/177Lu-DOTATATE. The administered activity was based on 3.7 GBq/m2 body surface area in three to five cycles, with amino acid infusion for nephroprotection.
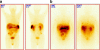
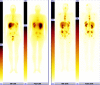
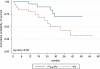
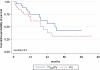
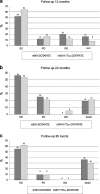
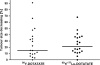
Results: The median overall survival time in group A was 26.2 months while in group B median survival was not reached. Overall survival was significantly higher in group B (p=0.027). Median event-free survival time in group A was 21.4 months and in group B 29.4 months (p>0.1). At the 12-month follow-up, comparison of group A vs group B showed stable disease (SD) in 13 vs 16 patients, disease regression (RD) in 5 vs 3 patients and disease progression (PD) in 3 vs 4 patients; 4 and 2 patients died, respectively. The 24-month follow-up results were SD in nine vs ten patients, RD in one patient vs none and PD in four patients in both groups; three and four patients died, respectively. Side effects were rare and mild.
Conclusion: The results indicate that therapy with tandem radioisotopes (90Y/177Lu-DOTATATE) provides longer overall survival than with a single radioisotope (90Y-DOTATATE) and the safety of both methods is comparable.
Figures

Comment in
-
90Y/177Lu-DOTATATE therapy: survival of the fittest?Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011 Oct;38(10):1785-7. doi: 10.1007/s00259-011-1878-x. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011. PMID: 21755369 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Radiation dosimetry is a necessary ingredient for a perfectly mixed molecular radiotherapy cocktail.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012 Mar;39(3):548-9. doi: 10.1007/s00259-011-2036-1. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22241725 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dharmsathaphorn K, Sherwin RS, Cataland S, Jaffe B, Dobbins J. Somatostatin inhibits diarrhea in the carcinoid syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1980;92:68–69. - PubMed
-
- Rinke A, Muller H-H, Schade-Brittinger C, et al. Placebo-controlled, double-blind, prospective, randomized study on the effect of octreotide LAR in the control of tumor growth in patients wit metastatic neuroendocrine midgut tumors: a report from the PROMID Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4656–4663. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.8510. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kwekkeboom D, Krenning EP, de Jong M. Peptide receptor imaging and therapy. J Nucl Med. 2000;41:1704–1713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

