Lung surfactant protein A (SP-A) interactions with model lung surfactant lipids and an SP-B fragment
- PMID: 21553841
- PMCID: PMC3104520
- DOI: 10.1021/bi200167d
Lung surfactant protein A (SP-A) interactions with model lung surfactant lipids and an SP-B fragment
Abstract
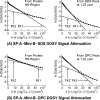
Surfactant protein A (SP-A) is the most abundant protein component of lung surfactant, a complex mixture of proteins and lipids. SP-A performs host defense activities and modulates the biophysical properties of surfactant in concerted action with surfactant protein B (SP-B). Current models of lung surfactant mechanism generally assume SP-A functions in its octadecameric form. However, one of the findings of this study is that when SP-A is bound to detergent and lipid micelles that mimic lung surfactant phospholipids, it exists predominantly as smaller oligomers, in sharp contrast to the much larger forms observed when alone in water. These investigations were carried out in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), dodecylphosphocholine (DPC), lysomyristoylphosphatidylcholine (LMPC), lysomyristoylphosphatidylglycerol (LMPG), and mixed LMPC + LMPG micelles, using solution and diffusion nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. We have also probed SP-A's interaction with Mini-B, a biologically active synthetic fragment of SP-B, in the presence of micelles. Despite variations in Mini-B's own interactions with micelles of different compositions, SP-A is found to interact with Mini-B in all micelle systems and perhaps to undergo a further structural rearrangement upon interacting with Mini-B. The degree of SP-A-Mini-B interaction appears to be dependent on the type of lipid headgroup and is likely mediated through the micelles, rather than direct binding.
Figures



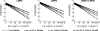

Similar articles
-
Structure of mini-B, a functional fragment of surfactant protein B, in detergent micelles.Biochemistry. 2007 Oct 2;46(39):11047-56. doi: 10.1021/bi7011756. Epub 2007 Sep 11. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17845058
-
NMR structures of the C-terminal segment of surfactant protein B in detergent micelles and hexafluoro-2-propanol.Biochemistry. 2004 Dec 7;43(48):15187-94. doi: 10.1021/bi0481895. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15568810
-
Combining precision spin-probe partitioning with time-resolved fluorescence quenching to study micelles. Application to micelles of pure lysomyristoylphosphatidylcholine (LMPC) and LMPC mixed with sodium dodecyl sulfate.Chem Phys Lipids. 2006 Jul;142(1-2):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2006.02.003. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Chem Phys Lipids. 2006. PMID: 16569402
-
Hydrophobic surfactant proteins and their analogues.Neonatology. 2007;91(4):303-10. doi: 10.1159/000101346. Epub 2007 Jun 7. Neonatology. 2007. PMID: 17575474 Review.
-
Protein-lipid interactions and surface activity in the pulmonary surfactant system.Chem Phys Lipids. 2006 Jun;141(1-2):105-18. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2006.02.017. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Chem Phys Lipids. 2006. PMID: 16600200 Review.
Cited by
-
Surfactant protein A alters endosomal trafficking of influenza A virus in macrophages.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 7;14:919800. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.919800. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36960051 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Dermal Fibroblasts Attenuate Inflammation in a Murine Model of Acute Lung Injury.Adv Mater. 2023 Jul;35(28):e2210579. doi: 10.1002/adma.202210579. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Adv Mater. 2023. PMID: 37119468 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the N-terminal seven residues of surfactant protein B (SP-B).PLoS One. 2013 Sep 2;8(9):e72821. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072821. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24023779 Free PMC article.
-
SP-A binding to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein using hybrid quantum and classical in silico modeling and molecular pruning by Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) Based MaxCut with ZDOCK.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 13;13:945317. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.945317. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36189278 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Aging-Related Emphysematous and Lymphoma-Like Lesions is Enhanced by the Lack of Secretoglobin 3A2 in Mouse Lungs.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022 May 26;17:1247-1260. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S330170. eCollection 2022. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022. PMID: 35651829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sueishi K.; Benson B. J. (1981) Isolation of a major apolipoprotein of canine and murine pulmonary surfactant. Biochemical and immunochemical characteristics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 665, 442–453. - PubMed
-
- Casals C., and Garcia-Verdugo I. (2005) Molecular and functional properties of surfactant protein A in Lung Surfactant Function and Disorder (Nag K., and Lenfant C., Eds.) pp 59–86, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, FL.
-
- Crouch E.; Wright J. R. (2001) Surfactant proteins A and D and pulmonary host defense. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 63, 521–554. - PubMed
-
- Lawson P. R.; Reid K. B. (2000) The roles of surfactant proteins A and D in innate immunity. Immunol. Rev. 173, 66–78. - PubMed
-
- Kuroki Y.; Takahashi M.; Nishitani C. (2007) Pulmonary collectins in innate immunity of the lung. Cell. Microbiol. 9, 1871–1879. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

