Early age alcohol use and later alcohol problems in adolescents: individual and peer mediators in a bi-national study
- PMID: 21553944
- PMCID: PMC3189291
- DOI: 10.1037/a0023320
Early age alcohol use and later alcohol problems in adolescents: individual and peer mediators in a bi-national study
Abstract
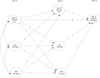
This paper examines whether there is cross-national similarity in the longitudinal relationship between early age alcohol use and adolescent alcohol problems. Potential mechanisms underlying this relationship also are examined, testing adolescent alcohol use, low self-regulation, and peer deviance as possible mediators. Students (N = 1,945) participating in the International Youth Development Study, a longitudinal panel survey study, responded to questions on alcohol use and influencing factors, and were followed annually over a 3-year period from 2002 to 2004 (98% retention rate). State-representative, community student samples were recruited in grade 7 in Washington State, United States (US, n = 961, 78% of those eligible; Mage = 13.09, SD = .44) and Victoria, Australia (n = 984, 76% of those eligible; Mage = 12.93, SD = .41). Analyses were conducted using multiple-group structural equation modeling. In both states, early age alcohol use (age 13) had a small but statistically significant association with subsequent alcohol problems (age 15). Overall, there was little evidence for mediation of early alcohol effects. Low self-regulation prospectively predicted peer deviance, alcohol use, and alcohol problems in both states. Peer deviance was more positively related to alcohol use and low self-regulation among students in Victoria compared to students in Washington State. The small but persistent association of early age alcohol use with alcohol problems across both samples is consistent with efforts to delay alcohol initiation to help prevent problematic alcohol use. Self-regulation was an important influence, supporting the need to further investigate the developmental contribution of neurobehavioral disinhibition.
Figures

References
-
- Bauman KE, Ennett ST. On the importance of peer influence for adolescent drug use: Commonly neglected considerations. Addiction. 1996;91(2):185–198. - PubMed
-
- Browne MW, Cudeck R. Alternative ways of assessing model fit. In: Bollen KA, Long JS, editors. Testing structural equation models. Newbury Park, CA: Sage; 1993. pp. 136–162.
-
- Catalano RF, Hawkins JD. The social development model: A theory of antisocial behavior. In: Hawkins JD, editor. Delinquency and crime: Current theories. New York: Cambridge University Press; 1996. pp. 149–197.
-
- Clark D, Kirisci L, Tarter RE. Adolescent versus adult onset and the development of substance use disorders in males. Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 1998;49:115–121. - PubMed

