Anabolic androgenic steroid abuse: multiple mechanisms of regulation of GABAergic synapses in neuroendocrine control regions of the rodent forebrain
- PMID: 21554430
- PMCID: PMC3168686
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2011.02151.x
Anabolic androgenic steroid abuse: multiple mechanisms of regulation of GABAergic synapses in neuroendocrine control regions of the rodent forebrain
Erratum in
- J Neuroendocrinol. 2012 May;24(5):849
Abstract
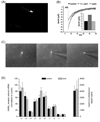
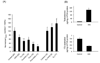
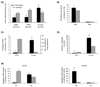
Anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS) are synthetic derivatives of testosterone originally developed for clinical purposes but are now predominantly taken at suprapharmacological levels as drugs of abuse. To date, almost 100 different AAS compounds that vary in metabolic fate and physiological effects have been designed and synthesised. Although they are administered for their ability to enhance muscle mass and performance, untoward side effects of AAS use include changes in reproductive and sexual behaviours. Specifically, AAS, depending on the type of compound administered, can delay or advance pubertal onset, lead to irregular oestrous cyclicity, diminish male and female sexual behaviours, and accelerate reproductive senescence. Numerous brains regions and neurotransmitter signalling systems are involved in the generation of these behaviours, and are potential targets for both chronic and acute actions of the AAS. However, critical to all of these behaviours is neurotransmission mediated by GABA(A) receptors within a nexus of interconnected forebrain regions that includes the medial preoptic area, the anteroventral periventricular nucleus and the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. We review how exposure to AAS alters GABAergic transmission and neural activity within these forebrain regions, taking advantage of in vitro systems and both wild-type and genetically altered mouse strains, aiming to better understand how these synthetic steroids affect the neural systems that underlie the regulation of reproduction and the expression of sexual behaviours.
© 2011 The Authors. Journal of Neuroendocrinology © 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Basaria S, Wahlstrom JT, Dobs AS. Clinical review 138: Anabolic-androgenic steroid therapy in the treatment of chronic diseases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:5108–5117. - PubMed
-
- Shahidi NT. A review of the chemistry, biological action, and clinical applications of anabolic-androgenic steroids. Clin Ther. 2001;23:1355–1390. - PubMed
-
- Kochakian C, Yesalis CE. Anabolic-androgenic steroids: a historical perspective and definition. In: Yesalis CE, editor. Anabolic Steroids in Sport and Exercise. Champaign: Human Kinetics; 2000. pp. 4–33.
-
- Llewellyn W. Body of Science. 6th Edition. Jupiter, FL: 2007. Anabolics; pp. vii–ix.
-
- Trenton AJ, Currier GW. Behavioural manifestations of anabolic steroid use. CNS Drugs. 2005;19:571–595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

