Unique ganglioside binding by botulinum neurotoxins C and D-SA
- PMID: 21554541
- PMCID: PMC3170675
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08166.x
Unique ganglioside binding by botulinum neurotoxins C and D-SA
Abstract
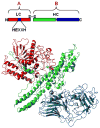
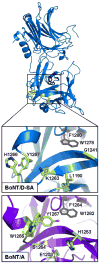
The botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs) are the most potent protein toxins for humans. There are seven serotypes of BoNTs (A-G), based on a lack of cross-antiserum neutralization. The BoNT/C and BoNT/D serotypes include mosaic toxins that are organized as D-C and C-D toxins. One BoNT D-C mosaic toxin, BoNT/D-South Africa (BoNT/D-SA), was not fully neutralized by immunization with a vaccine composed of either prototype BoNT/C-Stockholm or BoNT/D-1873. Whereas several BoNT serotypes utilize dual receptors (gangliosides and proteins) to bind to and enter neurons, the basis for BoNT/C and BoNT/D entry into neurons is less well understood. Recent studies solved the crystal structures of the receptor-binding domains of BoNT/C, BoNT/D, and BoNT/D-SA. Comparative structural analysis showed that BoNT/C, BoNT/D and BoNT/D-SA lacked components of the ganglioside-binding pocket that exists within other BoNT serotypes. With the use of structure-based alignments, biochemical analyses, and cell-binding approaches, BoNT/C and BoNT/D-SA have been shown to possess a unique ganglioside-binding domain, the ganglioside-binding loop. Defining how BoNTs enter host cells provides insights towards understanding the evolution and extending the potential therapeutic and immunological values of the BoNT serotypes.
© 2011 The Authors Journal compilation © 2011 FEBS.
Figures


References
-
- Singh BR, Gimenez JA, DasGupta BR. Comparative molecular topography of botulinum neurotoxins from Clostridium butyricum and Clostridium botulinum type E. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1077:119–126. [pii] - PubMed
-
- Lacy DB, Tepp W, Cohen AC, DasGupta BR, Stevens RC. Crystal structure of botulinum neurotoxin type A and implications for toxicity. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 1998;5:898–902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

