IsoBED: a tool for automatic calculation of biologically equivalent fractionation schedules in radiotherapy using IMRT with a simultaneous integrated boost (SIB) technique
- PMID: 21554675
- PMCID: PMC3117739
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-30-52
IsoBED: a tool for automatic calculation of biologically equivalent fractionation schedules in radiotherapy using IMRT with a simultaneous integrated boost (SIB) technique
Abstract
Background: An advantage of the Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT) technique is the feasibility to deliver different therapeutic dose levels to PTVs in a single treatment session using the Simultaneous Integrated Boost (SIB) technique. The paper aims to describe an automated tool to calculate the dose to be delivered with the SIB-IMRT technique in different anatomical regions that have the same Biological Equivalent Dose (BED), i.e. IsoBED, compared to the standard fractionation.
Methods: Based on the Linear Quadratic Model (LQM), we developed software that allows treatment schedules, biologically equivalent to standard fractionations, to be calculated. The main radiobiological parameters from literature are included in a database inside the software, which can be updated according to the clinical experience of each Institute. In particular, the BED to each target volume will be computed based on the alpha/beta ratio, total dose and the dose per fraction (generally 2 Gy for a standard fractionation). Then, after selecting the reference target, i.e. the PTV that controls the fractionation, a new total dose and dose per fraction providing the same isoBED will be calculated for each target volume.
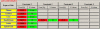
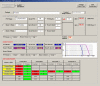
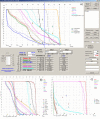
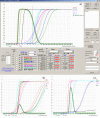
Results: The IsoBED Software developed allows: 1) the calculation of new IsoBED treatment schedules derived from standard prescriptions and based on LQM, 2) the conversion of the dose-volume histograms (DVHs) for each Target and OAR to a nominal standard dose at 2Gy per fraction in order to be shown together with the DV-constraints from literature, based on the LQM and radiobiological parameters, and 3) the calculation of Tumor Control Probability (TCP) and Normal Tissue Complication Probability (NTCP) curve versus the prescribed dose to the reference target.
Figures



References
-
- Ang KK, Peters LJ. Concomitant boost radiotherapy in the treatment of head and neck cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 1992;2:31–33. doi: 10.1016/S1053-4296(05)80049-9. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

