Physical mapping and BAC-end sequence analysis provide initial insights into the flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) genome
- PMID: 21554714
- PMCID: PMC3113786
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-217
Physical mapping and BAC-end sequence analysis provide initial insights into the flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) genome
Abstract
Background: Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) is an important source of oil rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have proven health benefits and utility as an industrial raw material. Flax seeds also contain lignans which are associated with reducing the risk of certain types of cancer. Its bast fibres have broad industrial applications. However, genomic tools needed for molecular breeding were non existent. Hence a project, Total Utilization Flax GENomics (TUFGEN) was initiated. We report here the first genome-wide physical map of flax and the generation and analysis of BAC-end sequences (BES) from 43,776 clones, providing initial insights into the genome.
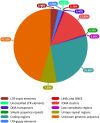
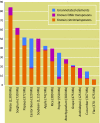
Results: The physical map consists of 416 contigs spanning ~368 Mb, assembled from 32,025 fingerprints, representing roughly 54.5% to 99.4% of the estimated haploid genome (370-675 Mb). The N50 size of the contigs was estimated to be ~1,494 kb. The longest contig was ~5,562 kb comprising 437 clones. There were 96 contigs containing more than 100 clones. Approximately 54.6 Mb representing 8-14.8% of the genome was obtained from 80,337 BES. Annotation revealed that a large part of the genome consists of ribosomal DNA (~13.8%), followed by known transposable elements at 6.1%. Furthermore, ~7.4% of sequence was identified to harbour novel repeat elements. Homology searches against flax-ESTs and NCBI-ESTs suggested that ~5.6% of the transcriptome is unique to flax. A total of 4064 putative genomic SSRs were identified and are being developed as novel markers for their use in molecular breeding.
Conclusion: The first genome-wide physical map of flax constructed with BAC clones provides a framework for accessing target loci with economic importance for marker development and positional cloning. Analysis of the BES has provided insights into the uniqueness of the flax genome. Compared to other plant genomes, the proportion of rDNA was found to be very high whereas the proportion of known transposable elements was low. The SSRs identified from BES will be valuable in saturating existing linkage maps and for anchoring physical and genetic maps. The physical map and paired-end reads from BAC clones will also serve as scaffolds to build and validate the whole genome shotgun assembly.
Figures

References
-
- Zohary D, Hopf M. Domestication of plants in the old world. 3. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2000.
-
- Diederichsen A, Richards K. In: Flax, the genus Linum. Muir AD, Westcott ND, editor. New York: Taylor and Francis; 2003. Cultivated flax and the genus Linum L. Taxonomy and germplasm conservation; pp. 22–54.
-
- Evans GM, Rees H, Snell CL, Sun S. The relationship between nuclear DNA amount and the duration of the mitotic cycle. Chromosomes Today. 1972;3:24–31.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

