Sex, drugs and gluttony: how the brain controls motivated behaviors
- PMID: 21554895
- PMCID: PMC3107928
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.04.057
Sex, drugs and gluttony: how the brain controls motivated behaviors
Abstract
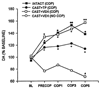
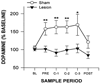
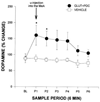
Bart Hoebel has forged a view of an integrated neural network that mediates both natural rewards and drug use. He pioneered the use of microdialysis, and also effectively used electrical stimulation, lesions, microinjections, and immunohistochemistry. He found that feeding, stimulant drug administration, and electrical stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus (LH) all increased dopamine (DA) release in the nucleus accumbens (NAc). However, whereas DA in the NAc enhanced motivation, DA in the LH inhibited motivated behaviors. The Hull lab has pursued some of those ideas. We have suggested that serotonin (5-HT) in the perifornical LH inhibits sexual behavior by inhibiting orexin/hypocretin neurons (OX/HCRT), which would otherwise excite neurons in the mesocorticolimbic DA tract. We have shown that DA release in the medial preoptic area (MPOA) is very important for male sexual behavior, and that testosterone, glutamate, nitric oxide (NO) and previous sexual experience promote MPOA DA release and mating. Future research should follow Bart Hoebel's emphasis on neural systems and interactions among brain areas and neurotransmitters.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dopamine and serotonin: influences on male sexual behavior.Physiol Behav. 2004 Nov 15;83(2):291-307. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.08.018. Physiol Behav. 2004. PMID: 15488546 Review.
-
Hormone-neurotransmitter interactions in the control of sexual behavior.Behav Brain Res. 1999 Nov 1;105(1):105-16. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(99)00086-8. Behav Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10553694 Review.
-
Dopamine, the medial preoptic area, and male sexual behavior.Physiol Behav. 2005 Oct 15;86(3):356-68. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.08.006. Epub 2005 Aug 30. Physiol Behav. 2005. PMID: 16135375 Review.
-
Lateral hypothalamic serotonin inhibits nucleus accumbens dopamine: implications for sexual satiety.J Neurosci. 1999 Sep 1;19(17):7648-52. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-17-07648.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10460270 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine release in the medial preoptic area is related to hormonal action and sexual motivation.Behav Neurosci. 2010 Dec;124(6):773-9. doi: 10.1037/a0021490. Behav Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21133533 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic influences on adolescent sexual behavior: Why genes matter for environmentally oriented researchers.Psychol Bull. 2014 Mar;140(2):434-65. doi: 10.1037/a0033564. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Psychol Bull. 2014. PMID: 23855958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroanatomy and function of human sexual behavior: A neglected or unknown issue?Brain Behav. 2019 Dec;9(12):e01389. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1389. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 31568703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors associated with sexual arousal, sexual sensation seeking and sexual satisfaction among female African American adolescents.Sex Health. 2013 Dec;10(6):512-21. doi: 10.1071/SH13005. Sex Health. 2013. PMID: 24262218 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic Responses to Cocaine and Food Cues in Individuals with Cocaine Dependence.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019 Dec 1;22(12):754-764. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyz044. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31420667 Free PMC article.
-
Reward-based hypertension control by a synthetic brain-dopamine interface.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Nov 5;110(45):18150-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312414110. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24127594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoebel BG, Teitelbaum P. Hypothalamic control of feeding and self-stimulation. Science. 1962;135:375–377. - PubMed
-
- Caggiula AR, Hoebel BG. “Copulation-reward site” in the posterior hypothalamus. Science. 1966;153:1284–1285. - PubMed
-
- Zemlan FP, Trulson ME, Howell R, Hoebel BG. Influence of p-chloroamphetamine on female sexual reflexes and brain monoamine levels. Brain Res. 1977;123:347–356. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez L, Hoebel BG. Feeding and hypothalamic stimulation increase dopamine turnover in the accumbens. Physiol Behav. 1988;44:599–606. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez L, Hoebel BG. Feeding can enhance dopamine turnover in the prefrontal cortex. Brain Res Bull. 1990;25:975–979. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

