Promise of resveratrol for easing status epilepticus and epilepsy
- PMID: 21554899
- PMCID: PMC3133838
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.04.008
Promise of resveratrol for easing status epilepticus and epilepsy
Abstract
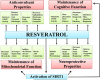
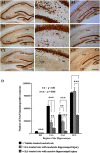
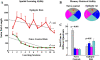
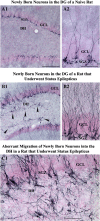
Resveratrol (RESV; 3,5,4'-tri-hydroxy stilbene), a naturally occurring phytoalexin, is found at a high concentration in the skin of red grapes and red wine. RESV mediates a wide-range of biological activities, which comprise an increased life span, anti-ischemic, anti-cancer, antiviral, anti-aging and anti-inflammatory properties. Studies in several animal prototypes of brain injury suggest that RESV is an effective neuroprotective compound. Ability to enter the brain after a peripheral administration and no adverse effects on the brain or body are other features that are appealing for using this compound as a therapy for brain injury or neurodegenerative diseases. The goal of this review is to discuss the promise of RESV for treating acute seizures, preventing the acute seizure or status epilepticus induced development of chronic epilepsy, and easing the chronic epilepsy typified by spontaneous recurrent seizures and cognitive dysfunction. First, the various beneficial effects of RESV on the normal brain are discussed to provide a rationale for considering RESV treatment in the management of acute seizures and epilepsy. Next, the detrimental effects of acute seizures or status epilepticus on the hippocampus and the implications of post-status epilepticus changes in the hippocampus towards the occurrence of chronic epilepsy and cognitive dysfunction are summarized. The final segment evaluates studies that have used RESV as a neuroprotective compound against seizures, and proposes studies that are critically needed prior to the clinical application of RESV as a prophylaxis against the development of chronic epilepsy and cognitive dysfunction after an episode of status epilepticus or head injury.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

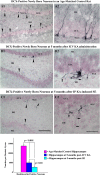
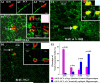
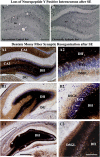

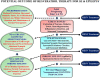
References
-
- Abd El-Mohsen M, Bayele H, Kuhnle G, Gibson G, Debnam E, Kaila Srai S, et al. Distribution of [3 H]trans-resveratrol in rat tissues following oral administration. Br J Nutr. 2006;96:62–70. - PubMed
-
- Abrous DN, Koehl M, Le Moal M. Adult neurogenesis: From precursors to network and physiology. Physiol Rev. 2005;85:523–569. - PubMed
-
- Aimone JB, Wiles J, Gage FH. Potential role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new memories. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:723–727. - PubMed
-
- Alessio A, Damasceno BP, Camargo CH, Kobayashi E, Guerreiro CA, Cendes F. Differences in memory performance and other clinical characteristics in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with and without hippocampal atrophy. Epilepsy Behav. 2004a;5:22–27. - PubMed
-
- Alessio A, Kobayashi E, Damasceno BP, Lopes-Cendes I, Cendes F. Evidence of memory impairment in asymptomatic individuals with hippocampal atrophy. Epilepsy Behav. 2004b;5:981–987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

